Chapter 2 Compliances – Secretarial Audit Compliance Management and Due Diligence ICSI Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Compliances – Secretarial Audit, Compliance Management and Due Diligence Study Material
Question 1.
Write short note on the following:
Compliance management (2016 Dec 5, 3 marks)
Answer:
Compliance management: A compliance management system is the method by which corporate manage the entire compliance process. It includes the compliance program, compliance audit, compliance report etc. and in other words it is called compliance solution.
Corporate compliance management involves a full process of research and analysis as well as investigation and evaluation. Such an exercise is undertaken in order to determine the potential issues and get a realistic view about how the entity is performing and how it is likely to perform in the future. Company secretaries with core competence in compliance and corporate governance play a crucial role in the corporate compliance management.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the compliances required with regard the following:
Significance of corporate compliance management. (June 2012, 4 marks)
Answer:
Significance of Corporate Compliance Management includes.
- Better compliance of the law.
- Real time status of legal/statutory compliances.
- Safety valve against unintended non compliances/prosecutions, etc.
- Cost savings by avoiding penalties/fines and minimizing litigation.
- Better brand image and positioning of the company in the market.
- Goodwill among the shareholders, investors and stakeholders.
- Real time status on the progress of pending litigation before the judicial /quasi-judicial forum.
- Enhanced credibility / credit worthiness that only a law abiding company can command.
Question 3.
Critically examine and comment of the following:
Corporate compliance management can add substantial business value only if compliance is done with due diligence. (June 2013, 4 marks)
Answer:
Corporate compliance management involves a full process of research and analysis as well as investigation and evaluation, which is nothing but a due diligence exercise. Such an exercise is undertaken in order to determine the potential issues and get a realistic view about how the entity is performing and how it is likely to perform in the future. Compliance with law and regulation must be managed as an integral part of any corporate strategy. – Space to write important points for revision
Question 4.
What are the areas required to be covered in establishing a compliance management framework? (June 2014, 7 marks)
Answer:
Establishment of compliance management framework
The Compliance Management encompasses
- Compliance Identification
- Compliance Ownership
- Compliance Awareness
- Compliance Reporting and
- Periodical Compliance MIS.
1. Compliance Identification
This process involves the identification of compliances under various legislations applicable to the company, in consultation with the functional heads.
2. Compliance Ownership
The next important aspect of compliance management is ownership. The ownership of the various compliances has to be described function wise and individual wise. Clear description of primary and secondary ownership is also very important. While the primary owner is mainly responsible for the compliance the secondary owner (usually the supervisor of the primary owner) has to supervise the compliance.
3. Compliance Awareness
The next important step in establishing a legal Compliance Management is creation of awareness of the various Legal Compliances amongst those responsible. Many a times compliances are handled by persons who are not fully aware of the requirements of the legislations and hence creating appropriate awareness amongst the owners is very important.
4. Compliance Reporting
Compliances or non-compliances should be communicated to the Concerned. Reporting of non-compliances ensures that appropriate corrective action is taken by the responsible person, Ex. Automated escalation emails in case of non compliance.
5. Process of Corporate Compliance Reporting (CCR)
The actual process of compiling the information under the various laws may vary from company to company and is dependent on various factors such as the number of units and scale of operations.
![]()
Question 5.
Critically examine and comment on the following.
Significance of corporate compliance management. (June 2014, 4 marks)
Answer:
Significance of Corporate Compliance Management
- Better compliance of the law.
- Real time status of legal/statutory compliances.
- Safety valve against unintended non compliances/ prosecutions, etc.
- Real time status on the progress of pending litigation before the judicial/authority or forum.
- Cost savings by avoiding penalties/fines and minimizing litigation.
- Better brand image and positioning of the company in the market.
- Enhanced credibility/creditworthiness that only a law abiding company can command.
- Goodwill among the shareholders, investors and stakeholders.
- Recognition as Good corporate citizen.
Question 6.
“The objective of Compliance Programme Template is to help the secretarial auditor in evaluating the critical aspects of compliance management.” Explain. (Dec 2017, 6 marks)
Answer:
“The Objective of Compliance Programme Template is to help the secretarial auditor in evaluating the critical aspects of compliance management.” This statement is true.
Compliance management through systematic processes helps in achieving 100% compliance with letter and spirit. The objective of Compliance Programme is
- To establish and maintain centralised mechanism to ensure compliance with all applicable laws (both Indian and International).
- To establish and maintain effective co-ordination of functional units and the compliance department under the overall supervision of the Board.
- To incorporate changes in the existing applicable laws or introduction of new laws, into the compliance process in real time manner.
- Effective communication of the changes in the regulatory mandates to the applicable functional and other units in real time manner.
- To provide training on compliance requirements at regular intervals.
- To introduce and implement ethics programmes for Board, Senior Management and other staff members.
- To establish pro-active compliance risk management culture into the organisation.
- To establish effective monitoring and control systems.
- To adopt fair market practices.
- To establish mechanisms to prevent, detect, report and to respond to non compliances.
- To introduce effective whistle blowing mechanism.
- To establish compliance dashboard.
Question 7.
Define the following terms:
Corporate Compliance Committee (June 2018, 3 marks)
Answer:
The primary responsibility of the Corporate Compliance Committee is to oversee the company’s Corporate Compliance Program with respect to:
- Compliance with the laws, rules and regulations applicable to the company
- Compliance with the Company’s Code of Conduct;
- Compliance with Company’s policies and procedures;
- Compliance with established standards;
- Compliance with prevention and detection of fraud, misappropriation etc.
- Oversight of the risk management activities of the Company and the protection of stakeholders.
- Making recommendation to revise the compliance management programme.
![]()
Question 8.
The intent of the law makers is to be carried out in letter and spirit in complying with the regulatory requirements of Corporate Governance in a corporate. Elaborate this statement with explanations. (Dec 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
Good Corporate Governance demands compliance levels that match the intentions of legislature, expectations of stakeholders and requirements of regulators. The compliances, however, generally found to fall in three categories, i.e., Apparent Compliances, Adequate Compliances and Absolute Compliances.
Apparent compliance is a disguise form of non-compliance, which is worse than a non-compliance. The classic example for Apparent Compliances are generating documents such as notice, agenda, minutes on papers for board and general meeting which are not actually held.
Adequate compliance is compliance in letters. The aspects specified in law are complied in letters, without getting into the spirit of the law, e.g. box ticking practices.
Absolute compliances are those which are in line with the spirit and intent of the law. A typical example in this regard is demonstrating shareholder democracy as prescribed by law. When a company complies with law in spirit it gains public confidence as well.
In order to attain corporate sustainability and to ensure a level playing field with international market, corporates need to necessarily increase their level of compliance from apparent to adequate, thereby leading to the level of absolute compliances.
Question 9.
You are appointed as Compliance Officer in a listed company. An Independent Director asks you to describe the scope of Corporate Compliance. Prepare a brief note. (June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
From:
Compliance officer Mr.
___________________ Limited
To:
Mr.
Independent Director
Sub: Scope of Corporate Compliance
Dear Sir,
As desired, the note on the Corporate Compliance is as under:
Corporate compliances broadly include compliance of Corporate and Economic Laws, Securities Laws. Commercial Laws including Intellectual Property Rights Laws, Labour Laws, Tax Laws, Cyber Laws which is also known as the Information Technology Law, Pollution Control Laws, Industry Specified laws and all other laws affecting the company concerned depending upon the type of industry/activity. The broad coverage of laws includes the compliances of the following laws:
- Companies Act, 2013 and the Rules and Regulations framed thereunder, MCA-21 requirements and procedures
- Secretarial Standards/Accounting Standards/Cost Accounting Standards issued by ICSI/ICAI/IOMAI, respectively
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 and the various Notifications, Rules and Regulations framed thereunder
- Competition Act, 2002
- SEBI Act, 1992
- Securities (Contracts) Regulation Act, 1956 and rules made thereunder
- SEBI (Listing obligations and Disclosure Requirements)Regulations, 2015
- Depositories Act, 1996
- Intellectual Property Rights Laws
- Income Tax Act, 1961
- Customs Act, 1962
- GST Laws
- Labour Laws
- Environment Laws
- Industry Specific Laws
- Local Laws include Municipal and Civic Administration Laws, Shops and
- Establishments etc.
Regards,
___________
Compliance Officer
_______________ Ltd.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the compliances under Securities Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) [SEBI (LODR] Regulations, 2015 relevant to the common obligations to any listed entity indicating the time period and event of each. (June 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Regulations 5 to 14 of Chapter III of the SEBI (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements), 2015 provides for the following Common Obligation of Listed Entities which require compliance:
| Compliance | Time Period | Event |
| 1. Submission of Compliance Certificate to the Exchange Regulation 7(3) | Within thirty days from the end of the financial year | Submission of Compliance Certificate to Stock Exchange certifying that all activities in relation to share transfer facility are maintained either in house or by Registrar to an issue and share transfer agent registered with the Board. |
| 2. Appointment/change of Share Transfer Agent Regulation7(5) | Intimate to the Stock Exchange such appointment or change within 7 days of entering into agreement. | Company can manage in house Share Transfer Facility. But as and when the total number of holders of securities of the listed entity exceeds one lac, the listed entity shall appoint Share Transfer Agent. |
| 3. Grievance Redressal Mechanism Regulation 13 | Within 21 days of the end of the each quarter. | The listed entity shall file with the recognized stock exchange(s) a statement giving
|
However, the other requirements under this chapter are continuous in nature such as appointment of a qualified company secretary as the compliance officer, policy for preservation of documents, electronic mode of payment facility for payment of dividend or interest or redemption or repayment. These requirements do not provide for any time lines and the compliance of such obligations are required on a continuous basis.
Question 11.
Jindal Brothers has constituted a Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) under the LLP Act, 2008. There are total 3 partners in the Firm. Jindal Brothers has approached you for maintaining the various books of accounts. Being a Company Secretary, make a brief note on Section 34 read with Rule 24, as per compliance requirement, under the LLP Act, 2008. (Dec 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
Brief Note on Section 34 read with Rule 24, as per compliance requirement, under the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008:
According to Section 34 of Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008, a Limited Liability Partnership shall maintain its books of accounts relating to its affairs for each year of its existence on cash basis or accrual basis and according to double entry system of accounting.
The LLP shall maintain its books of accounts at its registered office for a period of Eight years.
Rule 24 of Limited Liability Partnership Rules, 2009:
The Books of Accounts of a Limited Liability Partnership shall contain the following:
- particulars of all sums of money received and expended and the matters in respect of which the receipt and expenditure takes place;
- a record of the assets and liabilities;
- statements of cost of goods purchased, inventories, work-in-progress, finished goods and cost of goods sold: and
- any other particulars which the partners may decide.
Sub-rule (3) of Rule 24 of Limited Liability Partnership Rules, 2009: The books of account of a limited liability partnership are required to be preserved for eight years from the date on which they are made.
Sub-rule (17) of Rule 24 of Limited Liability Partnership Rules, 2009: The remuneration of an auditor appointed by the limited liability partnership shall be fixed by the designated partners or by following the procedure as laid down in the limited liability partnership agreement.
Sub-rule (4) Rule 24 of Limited Liability Partnership Rules, 2009: For the purposes of sub-section (3) of section 34, every limited liability partnership shall file the Statement of Account and Solvency in Form 8 with the Registrar, within a period of thirty days from the end of six months of the financial year to which the Statement of Account and Solvency relates.
Sub-section (4) of Section 34 of LLP Act, 2008 read with sub-rule (8) of Rule 24, Limited Liability Partnership Rules, 2009.
The following limited liability partnerships, shall be required to get its accounts audited:
- whose turnover in any financial year exceeds forty lakh rupees, or
- whose contribution exceeds twenty-five lakh rupees.
![]()
Question 12.
Odee Ltd., a listed company has appointed two independent directors. As part of its familiarization policy it provides key updates and background about the company to the newly appointed directors. The directors have requested you as the Company Secretary of the company to explain the process of Corporate Compliance Reporting. Explain the process. (Aug 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
Any corporate compliance management framework encompasses the various steps relating to Compliance Identification, Compliance Ownership, Compliance Awareness, Compliance Reporting and Periodical Compliance MIS.
Under various business structures, actual process of compiling the information under various laws vary from company to company and is dependent on various factors such as number of units and scale of operations, size of company, number of business activities etc.
A brief process of the Corporate Compliance Reporting (CCR) mechanism is as under:
- Functional heads for reporting of various laws have to be identified. For example- the Company Secretary would be the functional head for reporting of Company Law, Listing Regulations and Commercial Laws. Similarly, the head of the personnel department canreport the compliances of labour and industrial laws and fiscal law compliance would be the domain of head of the finance/accounts departments.
- Each of the functional heads may collect and classify the relevant information from the various units/ locations pertaining to their department and consolidate them in the form of a report.
- The report shall carry an affirmation from the functional heads that the said report has been prepared based on the inputs received from the various units/ offices and then list out the specific compliances/ ‘ non-compliances, as already circulated to the functional heads. Each of the functional heads should forward their respective compliance reports to the Company Secretary/Managing Director.
- The Company Secretary would then brief the Managing Director and with suitable inputs from the Company Secretary, the Managing Director would consolidate and present, under his signature, a comprehensive CCR to the board for its information, advice and noting. The whole process of CCR is contingent on the creation and implementation of comprehensive legal Management Information System (MIS).
In the process of the Compliance Reporting, the status of compliances or non-compliances, if any, should be communicated to the concerned functional head. Reporting of non-compliances ensures that appropriate corrective action can be timely taken by the responsible person.
Question 13.
What are the records to be preserved for a period of 21 i years and 5 years under Rules 27 of LLP Act? (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
As per Rule 27 of the Limited Liability Rules, 2009, subject to previous x approval order of Registrar, the records in the office of Registrar may be destroyed after the expiry of period specified preservation for 21 years and 5 years are as follows:
1. Records to be preserved for 21 years
All papers, registers, refund orders and correspondence relating to the limited liability partnership liquidation accounts.
2. Records to be preserved for 5 years:
- Registered documents of limited liability partnership which have been fully wound up and finally dissolved together with correspondence relating to such limited liability partnership;
- Copies of Government orders relating to limited liability partnership;
- Copies of statistical returns furnished to Government;
- Papers relating to legal proceedings from the date of disposal of the case and appeal, if any;
- All correspondences including correspondences relating to scrutiny of accounts, annual returns, prosecutions, reports to the Central Government and the Tribunal and the correspondences relating to complaints.
In case of prosecution matter, the date is to be recorded from the date of disposal of the case and appeal, if any.
![]()
Question 14.
You are a Company Secretary of a Listed Company, where the prior notice is required to be sent to stock exchange before the Board Meeting. Kindly list out the matters under consideration for the meeting where at least 2 days prior notice of the Board Meeting is to be intimated by the Company to the Stock Exchange. (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
According to Regulation 29 of SEBI (Listing Obligation and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015: Prior intimating to stock exchange at least 2 working days in advance excluding the date of intimation & date of board meeting is required to be made for the following matters:
- Fund raising by following ways of further Public Offer, Rights Issue, American Depository Receipts/Global Depository Receipts/Foreign Currency ConvertibleBonds, qualified institutions placement, debt issue, preferential issue or any other method and for determination of issue price:
- Proposal for Buyback of Securities;
- Proposal for voluntary delisting of listed entity from the Stock Exchange(s)
- Declaration/Recommendation of Dividend, Issue of Convertible Securities including convertible debentures or of debentures carrying a right to subscribe to equity shares or the passing over of dividend.
- Proposal for declaration of Bonus Securities.
Question 15.
Why are the following registers maintained in a company and under what rules?
CHG-7, MGT-2, MBP-3, SH-3, PAS-5. (June 2022, 5 marks)
Question 16.
A subsidiary to a listed company, irrespective of its registered status, to a large extent is treated as a listed company by the authorities. As the Secretarial advisor and auditor of XYZ Ltd., which is a Public Ltd. company and a subsidiary to a listed company ABC Ltd., how would you ensure the compliance of Corporate Governance requirements by XYZ Ltd., with reference to the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015? (Dec 2018, 5 marks)
Answer:
As per the Regulation 24 of the SEBI (LODR) Regulations, 2015 the following compliances are required to be ensured by a subsidiary of a listed company with reference to Corporate Governance:
1. At least one independent director on the board of directors of the listed entity shall be a director on the board of directors of an unlisted material subsidiary, or not incorporated in India.
2. The audit committee of the listed entity shall also review the financial statements, in particular, the investments made by the unlisted subsidiary.
3. The minutes of the meetings of the board of directors of the unlisted subsidiary shall be placed at the meeting of the board of directors of the listed entity.
4. The management of the unlisted subsidiary shall periodically bring to the notice of the board of directors of the listed entity, a statement of all significant transactions and arrangements entered into by the unlisted subsidiary.
Explanation: For the purpose of this regulation, the term significant transaction or arrangement shall mean any individual transaction or arrangement that exceeds or is likely to exceed ten percent of the total revenues or total expenses or total assets or total liabilities, as the case may be, of the unlisted subsidiary for the immediately preceding accounting year.
5. A listed entity shall not dispose of shares in its material subsidiary resulting in reduction of its shareholding (either on its own or together with other subsidiaries) to less than or equal to fifty percent or cease the exercise of control over the subsidiary without passing a special resolution in its General Meeting except in cases where such divestment is made under a scheme of arrangement duly approved by a Court/Tribunal, or under a resolution plan duly approved under section 31 of the Insolvency Code and such an event is disclosed to the recognized stock exchanges within one day of the resolution plan being approved.
6. Selling, disposing and leasing of assets amounting to more than twenty percent of the assets of the material subsidiary on an aggregate basis during a financial year shall require prior approval of shareholders by way of special resolution, unless the sale/disposal/lease is made under a scheme of arrangement duly approved by a Court/Tribunal, [or under a resolution plan duly approved under section 31 of the Insolvency Code and such an event is disclosed to the recognized stock exchanges within one day of the resolution plan being approved].
7. Where a listed entity has a listed subsidiary, which is itself a holding company, the provisions of this regulation shall apply to the listed subsidiary in so far as its subsidiaries are concerned.
As a Secretarial advisor and auditor of XYZ Ltd., which is a Public Ltd. company and a subsidiary to a Listed company ABC i_td., I would focus on checking the compliance by XYZ Ltd. of the above cited points and thereby ensure, the compliance of Corporate Governance requirements by XYZ Ltd., with reference to the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015.
![]()
Question 17.
Zen Pvt. Limited had a paid up share capital of ?35 crore in the previous year. The Company Secretary advises the Company that it is mandatory to appoint the auditor as per the requirements of Sec. 139 (2) of the Companies Act, 2013. The company is having public borrowings viz. from banks ₹ 25 crore financial institutions ₹ 20 crore and public deposits of ₹ 7.5 crore. Examine the requirement of applicability of mandatory term/ rotation in the appointment of auditor with reference to the changed scenario since June, 2017. (Dec 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
Provisions of Section 139 (2) of the Companies Act 2013 and Rule 5 of the Companies (Audit and Auditors) Rules, 2014, as amended, deals with applicability of mandatory term / rotation in the appointment of auditor and the said provision is applicable to the following class of companies:
(a) All unlisted public companies having paid up share capital of Rupees 10 crore or more;
(b) All private limited companies having paid up share capital of Rupees 50 crore or more;
(c) All companies having paid up share capital below the threshold limit mentioned in (a) and (b) above but having public borrowings from financial institutions, banks or public deposits of 50 crore or more.
Accordingly, Zen Pvt. Limited will get be covered as per provision (c) above and therefore, it is mandatorily required to rotate the Auditor as per the provisions of Section 139 (2) of the Companies Act, 2013.
Question 18.
You have been appointed as Company Secretary of XYZ Ltd., a listed company, having diversified business and multi-operational branch offices. On joining your office, you observed that under the prevailing scenario a comprehensive compliance, management system is necessary. Prepare a checklist that should be considered by you about the desired system. What would be your responsibility as Company Secretary of the Company in due compliance of the desired system? (Dec 2019, 5 marks)
Answer:
The compliance system and processes in a company are dependent mainly on the following factors:
(a) Nature of business(es).
(b) Geographical domain of its area of operation(s).
(c) Size of the company both in terms of operations as well as investments, technology, multiplicity of business activities and manpower employed.
(d) Jurisdictions in which it operates.
(e) Whether the company is a listed company or not.
(f) Regulatory authority (i.es) in respect of its business operations.
(g) Nature of the company viz., private, public, government company, etc. A Company Secretary is the ‘Compliance Manager’ of the company. It is he who ensures that the company is in total compliance with all regulatory provisions. Corporate disclosures, which play a vital role in enhancing corporate valuation, is the forte of a Company Secretary. These disclosures can be classified into statutory disclosures, non-statutory disclosures, specifies disclosures and continuous disclosures.
SEBI (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulation, 2015 spells out elaborately on various aspects of disclosures which are to be made by the company such as contingent liabilities, related party transactions, proceeds from initial public offerings, remuneration of directors and various details giving the threats, risks and opportunities under management discussion and analysis in the corporate governance report which is published in the annual accounts duly certified by the professional like company secretaries. A company secretary has to ensure that these disclosures are made to shareholders and other stakeholders in true letter and spirit.
The advisory services of the company secretaries impact to all components and activities of the compliance framework, as the business receives one point specialized support and advice to help manage its compliance risks more effectively. The company secretary plays a proactive advisory role as he advises management, local boards and committees, the compliance executor, and the employees.
The company secretary provide advice ori compliance risk, responsibilities, obligations, concerns and other compliance issues that are suitable for the business’ practices and operational constraints of the company.
The company secretary is the professional who guides the board and the company in all matters, renders advice in terms of,compliance and ensures that the board procedures are duly followed, best global practices are brought in and the organisation is taken forward towards good corporate citizenship.
The function of Company Secretary includes:
(a) to report to the Board about compliance with the provisions of this Act, the rules made thereunder and other laws applicable to the company;
(b) to ensure that the company complies with the applicable secretarial standards;
(c) to provide to the directors of the company, collectively and individually, such guidance as they may require, with regard to their duties, responsibilities and powers;
(d) to facilitate the convening of meetings and attend Board, committee and general meetings and maintain the minutes of these meetings;
(e) to obtain approvals from the Board, general meeting, the government and such other authorities as required under the provisions of the Act;
(f) to represent before various regulators, and other authorities under the Act in connection with discharge of various duties under the Act;
(g) to assist the Board in the conduct of the affairs of the company;
(h) to assist and advise the Board in ensuring good corporate governance and in complying with the corporate governance requirements and best practices;
(i) to discharge such other duties as have been specified under the Act or rules; and
(j) such other duties as may be assigned by the Board from time to time.
![]()
Question 19.
Jemez & Co. Ltd. has listed its Securitized Debt Instruments at a stock exchange. One of the directors has asked you, being the compliance officer of the company, to inform the obligations of the company regarding its Securitized Debt Instruments. Describe with reference to compliances under the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Listing Obligations and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015. (Dec 2020, 5 marks)
Answer:
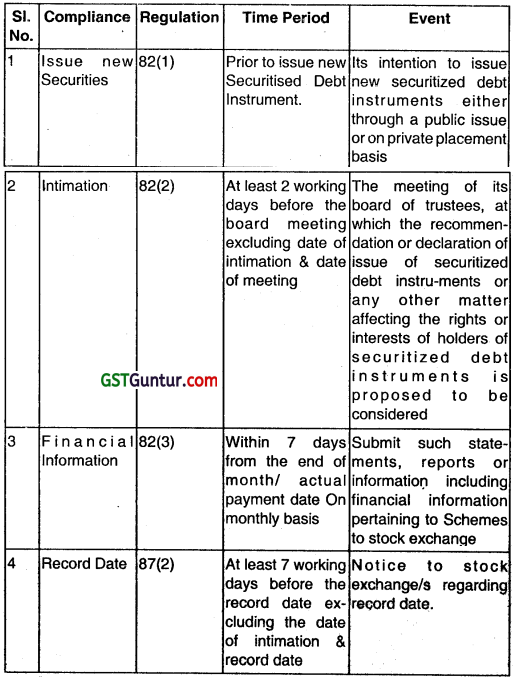
Question 20.
IT Ltd. acquired 99% equity shares in Zeb Ltd. on 1sl February, 2021. Amongst other compliances the Company Secretary informed the finance team that the consolidated Financial Statements of IT Ltd. are required to be prepared and presented to the Board. The CFO asks the Company Secretary to prepare a brief note on compliances relating to the Financial Statements and forms to be filed with Registrar of Companies for discussion with the Statutory auditors. Outline the key points to be covered in the note and indicate the relevant forms to be filed. (Aug 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
Preparing consolidated financial statement:
According to section 129(3) of Companies Act, 2013, where a company has one or more subsidiaries, it shall, in addition to its financial statements, prepare a consolidated financial statement.
Further, the company shall also attach along with its financial statement, a separate statement containing the salient features of the financial statement of its subsidiary in Form AOC-1.
Approval of Financial Statement by the Board:
According to section 134 of the Companies Act, 2013, the financial statement, including consolidated financial statement, shall be approved by the Board of Directors before the same being signed for and on behalf of the Board. The resolution approving the said financial statements shall be filled in e-form MGT -14 pursuant to Sec 117(3)(g) read with Sec 179(3) of the Act.
Placing the Financial Statements in AGM:
According to section 129(2) of the Companies Act, 2013, at every AGM of a company, the Board of Directors of the company shall lay before such meeting financial statements for the financial year.
Filling of Financial Statements with ROC:
As per Section 137 of Companies Act, 2013 & Rule 12(1) of Companies (Accounts) Rules, 2014, the company is required to file its financial statements, including consolidated financial statement along with all the required documents with the Registrar within 30 days of the date of AGM or in case financial statements are adopted in the adjourned AGM, within 30 days of the date of adjourned AGM.
If financial statements are not adopted at AGM dr adjourned AGM, such unadopted financial statements along with the required documents shall be filed with the Registrar within thirty days of the date of AGM and the Registrar shall take them in his records as provisional till the financial statements are filed with him after their adoption in the adjourned AGM for that purpose.
If AGM is not held for any year, the financial statements along with the documents required to be attached under section 137(1) duly signed along with the statement of facts and reasons for not holding the annual general meeting shall be filed with the Registrar in within 30 days of the last date before which the annual general meeting should have been held.
The Financial Statements shall be filled in E-form AOC-4 & E-form AOC-4 CFS.
![]()
Question 21.
Amit Krishna, a Company Secretary and Law Graduate by profession, was appointed as Company Secretary cum Compliance officer for Radha Raman Ltd. (a BSE Listed Company). The Company follows the Good Corporate Governance practices and resolution for each and every grievance of the Stakeholder of the Company . Under The SEBI (LODR) Regulations, 2015, what are the provisions there for Grievance Redressal Mechanism & Submission of Compliance Certificate to the Exchange? (Dec 2021, 5 marks)
Answer:
Grievance Redressal Mechanism: Regulation 13(3) of SEBI (Listing Obligation and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015 Time Period :The listed entity shall file with the recognised stock exchange(s) on a quarterly basis, within twenty one days from the end of each quarter, a statement giving the number of investor complaints pending at the beginning of the quarter, those received during the quarter, disposed of during the quarter and those remaining unresolved at the end of the quarter.
Events:
The Listed entity shall ensure that adequate steps are taken for expeditious Redressal of investor complaints.
The listed entity shall ensure that it is registered on the SCORES platform or such other electronic platform or system of the Board as shall be mandated from time to time, in order to handle investor complaints electronically in the manner specified by the Board.
The listed entity shall file with the recognized stock exchange(s) a statement giving:
- The number of investor complaints pending at the beginning of the quarter,
- Those received during the quarter,
- Disposed of during the quarter and
- Those remaining unresolved at the end of the quarter.
The same statement shall be placed before the Board of Directors quarterly
Submission of Compliance Certificate to the Exchange, Regulation 7(3) & (2) of SEBI (Listing Obligation and Disclosure Requirements) Regulations, 2015:
Time Period: Within 30 days of end of the financial year.
Events: Submission of Compliance Certificate to Stock Exchange certifying that all activities in relation to both physical and electronic share transfer facility are maintained either in house or by Registrar to an issue and share transfer agent registered with the Board.
Further the listed entity shall submit a compliance certificate to the exchange, duly signed by both the compliance officer of the listed entity and the authorised representative of the share transfer agent, wherever applicable.
Question 22.
Murthy, an Indian resident and citizen of India, has incorporated one person company under the Companies Act, 2013 at Mumbai with a paid up share capital of ₹ 40 lakh. During the financial year 2021-2022, turnover of the company was ₹ 1.35 crore. The director of this company has asked the Company Secretary about holding of board meetings, notice and quorum of board meetings and appointment of auditor. Explain the applicable section, rule and compliances for these matters. (June 2022, 5 marks)
Question 23.
List out the records which are required to be maintained by the LLPs under the LLP Act, 2008.
Answer:
Records to be preserved Permanently
- Incorporation document [Section 11 (1 )(b)] Permanent
- Notice of situation of registered office [Section 13] Permanent
- Information with regard to Limited Liability Permanent Partnership Agreement or any changes made therein [Section 23(2)]
- Notice of other address of any limited liability Permanent partnership at which documents to be served [Section 13(2)]
Records to be preserved for 21 Years:
All papers, registers, refund orders and correspondence relating to the limited liability partnership liquidation accounts to be preserved for 21 years.
Records to be preserved for 5 Years:
- Copies of Government orders relating to limited liability partnership; registered documents of limited liability partnership which have been fully wound up and finally dissolved together with correspondence relating to such limited liability partnership;
papers relating to legal proceedings from the date of disposal of the case and appeal, if any; - copies of statistical returns furnished to Government;
- all correspondences including correspondences relating to scrutiny of accounts, annual returns, prosecutions, reports to the Central Government and the Tribunal and the correspondences relating to complaints.
In case of prosecution matter, the date is to be recorded from the date of disposal of the case and appeal, if any.
Records to be preserved for 3 Years:
- All books, records and papers, other than those specified in other categories.
- Routine correspondence regarding payment of fees, additional filing fees and correspondence about the return of documents.
Preservation of Records under Annexure C of the LLP rules:
- Statement of compliance with requirements of the Act by an Advocate or Company Secretary or Chartered Accountant or Cost Accountant in whole-time practice and by any person who subscribed his name to the incorporation document [Section 11 (1 )(c)] – 5 years
- Notice of a person ceasing to be a partner and any change in the name or address of a partner – 5 years
- Registered documents relating to LLP struck off under Section 75 together with correspondence or copy of the order of restoration of the LLP into the register – 5 years
- Annual return of a limited liability partnership 5 years
- Consent of candidates to act as designated partner to be filed with the Registrar [section 7(4)] – 5 years
- Consent to act as a partner – 5 years
- Statement by all the partners of firm containing particulars of firm along with application for its conversion into limited liability partnership – 5 years
- Statement by all the shareholders containing particulars of private company/unlisted public company along with application for its conversion into limited liability partnership – 5 years
- Certified copy of the order(s) of the Tribunal under section 60/61/62.- 5 years
- Copy of the order of dissolution of a LLP by Tribunal [Section 63] -5 years
- Statement of Account and Solvency – 8 years
Records of foreign limited liability partnerships:
Registered documents of foreign limited liability partnerships which cease to have any place of business in India shall be destroyed after expiry of three years from the date such limited liability partnerships cease to have any place of business in India.
![]()
Question 2.
For which purpose Newspaper Advertisements required to be given/ published by the private companies under the provisions of Companies Act, 2013.
Answer:
Newspaper Advertisements required to be given/ published by the private companies under the provisions of Companies Act, 2013 for the following purposes:
- Application for Grant of License under section 8 by existing company
- Change in registered office from the Jurisdiction of one Registrar to another within the same state.
- Change in registered office from One State or Union Territory to another.
- Acceptance of Deposits.
- Closure of Foreign Register.
- Closure of Register of Members or debenture holders, Shareholders or other Security holders.
- Voting through Electronic means
- Postal Ballot
- Resolution requiring Special Notice
- Power to compromise or make arrangements with creditors and members.
Compliances Notes
Benefits of Corporate Compliance Management
- Better compliance of the law
- Real time status of legal/statutory compliances
- Safety valve against unintended non compliances/prosecutions, etc.
- Real time status on the progress of pending litigation before the judicial/quasi-judicial authority
- Cost saving by avoiding penalties/fines and minimizing litigation
- Better brand image and positioning of the company in the market
- Enhanced credibility/creditworthiness that only a law abiding company can command
- Goodwill among the shareholders, investors, and stakeholders.
- Recognition as Good corporate citizen.
Scope of Corporate Compliance
- Corporate compliance management broadly include compliance of:
- Corporate and Economic Laws
- Securities Law
- Commercial Laws including Intellectual Property Rights Laws
- Labour Laws
- Tax Laws
- Cyber Law which is also known as The Information Technology Law
- Pollution Control Laws
- Industry Specified laws
- All other Laws affecting the company concerned depending upon the type of industry/activity.
Activity Wise Compliances:
The activity wise compliances include the compliances relating to the Business Activities of the company such as Banking Company, Insurance Company, Housing Development Company, IFSC Company, NBFC, Section 8 Company, Producer Company, Chit Fund Company, Plantation Company etc.
These companies are governed under the Companies Act, 2013 as well as the Laws, Rules, Regulations under which they have been registered. The Companies Act, 2013 provides the specific provision, exemptions to such companies, however the additional compliance requirement may be imposed on these companies.
Sector Wise Compliances:
For the Sector wise compliances the Companies can be broadly divided in to the Agriculture and Allied Activities, Manufacturing, Construction, Power, Electricity; Gas and Water, Mining and Quarrying, Business Services, Real Estate and Renting, Trading, Community; Personal and Social Services, Transport; storage and communications, Finance, Insurance etc. these companies are governed under the Companies Act, 2013 along with the sector specific laws, Rules, Regulations, policies, procedures and State and Local laws applicable to the company.
Records to be preserved Permanently:
- Incorporation document [Section 11 (1 )(b)]
- Permanent Notice of situation of registered office [Section 13]
- Permanent Information with regard to Limited Liability Permanent Partnership Agreement or any changes made therein [Section 23(2)]
- Notice of other address of any limited liability Permanent partnership at which documents to be served [Section 13(2)]
Records to be preserved for 5 Years:
Copies of Government orders relating to limited liability partnership; registered documents of limited liability partnership which have been fully wound up and finally dissolved together with correspondence relating to such limited liability partnership;
- papers relating to legal proceedings from the date of disposal of the case and appeal, if any;
- copies of statistical returns furnished to Government;
- all correspondences including correspondences relating to scrutiny of accounts, annual returns, prosecutions, reports to the Central Government and the Tribunal and the correspondences relating to complaints.
In case of prosecution matter, the date is to be recorded from the date of disposal of the case and appeal, if any.
![]()
Some Purposes for which disclosures to be made at Website of the Company:
- Companies registered under Section 8 seeking conversion into any other kind
- Publication of name by Company
- Circular For Inviting Deposits from the public
- Closure of Register of Members or Debenture Holders or other Security Holders
- Notice of the General Meeting
- Postal Ballot
- Resolutions Requiring Special Notice
- Disclosures about Corporate Social Responsibility Policy (by a company to whom CSR is applicable)
- Notice of Resignation of director
- Advertisement of the notice of the meeting pursuant to exercise of power to Compromise or make arrangements with creditors and members.