Students should practice Cash Flow Statement – Corporate and Management Accounting CS Executive MCQ Questions with Answers based on the latest syllabus.
Cash Flow Statement – Corporate and Management Accounting MCQ
Question 1.
Dec 2014: In the cash flow statement, interest received by the company is classified as
(A) Operating activities
(B) Cash and cash equivalents
(C) Investing activities
(D) Financing activities
Answer:
(C) Investing activities
Question 2.
Dec 2014: In the cash flow statement, the dividend paid in the case of a financing company is classified as
(A) Operating activities
(B) Investing activities
(C) Financing activities
(D) Cash and cash equivalents
Answer:
(A) Operating activities
Question 3.
Dec 2014: From the following data, find the value of building sold during the year:
| Particulars | 31.32013 | 31.3.2014 |
| Land & building | 2,00,000 | 1,70,000 |
| Capital reserve | Nil | 20,000 |
A piece of land has been sold during the year and the profit on sale has been credited to capital reserve. Depreciation charged on the building during the year is ₹ 5,000; no additions have been made under this head during the year.
(A) ₹ 30,000
(B) ₹ 50,000
(C) ₹ 40,000
(D) ₹ 45,000
Hint:
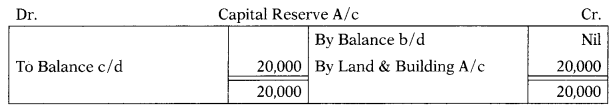
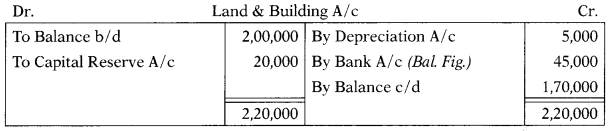
Answer:
(D) ₹ 45,000
Question 4.
June 2015: The following information pertains to Expert Ltd.:
| Particulars | 31.12.2013 | 31.12.2014 |
| Creditors | 86,600 | 98,400 |
| Outstanding expenses | 85,000 | 1,15,000 |
| Provision for tax | 1,50,000 | 1,60,000 |
| Debtors | 2,68,000 | 2,54,000 |
| Stock | 1,40,000 | 1,75,000 |
Net profit before working capital changes is ₹ 5,56,000. The cash flow from operating activities will be
(A) 4,26,800
(B) 5,76,800
(C) 5,35,200
(D) 4,16,800
Hint:
| Net profit before working capital changes | 5,56,000 |
| Increase in creditors | 11,800 |
| Increase in outstanding expenses | 30,000 |
| Decrease in debtor | 14,000 |
| Increase in stock | (35,000) |
| Cash generated from the operation | 5,76,800 |
| Income tax paid | (1,50,000) |
| Cash flows from operating activities | 4,26,800 |
Opening balance of provision for taxation deemed to be paid during the year.
Answer:
(A) 4,26,800
Question 5.
June 2015: In the case of a financial enterprise, interest received on debentures held as an investment is:
(A) Financing activity
(B) Investing activity
(C) Operating activity
Answer:
(C) Operating activity
Question 6.
June 2015: As per Accounting Standard-3, cash equivalents include –
(A) Treasury bills
(B) Commercial papers
(C) Money market funds
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 7.
June 2015: Cash payments to and on behalf of employees is an example of cash flow from –
(A) Operating activity
(B) Investing activity
(C) Financing activity
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Operating activity
Question 8.
June 2015: Net profit before working capital changes of Super Ltd. is ₹ 4,35,000. Changes in working capital during the year are as follows:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Decrease in stock | 2,58,000 |
| Decrease in bills payable | 8,400 |
| Increase in bills receivable | 38,800 |
| Increase in prepaid expenses | 2,500 |
| Increase in outstanding expenses | 7,800 |
Cash generated from operation for Super Ltd. will be:
(A) ₹ 2,18,900
(B) ₹ 7,45,500
(C) ₹ 6,51,100
(D) ₹ 2,34,500
Hint:
| Net profit before working capital changes | 4,35,000 |
| Decrease in stock | 2,58,000 |
| Decrease in bills payable | (8,400) |
| Increase in bills receivable | (38,800) |
| Increase in prepaid expenses | (2,500) |
| Increase in outstanding expenses | 7,800 |
| 6,51,100 |
Answer:
(C) ₹ 6,51,100
Question 9.
June 2015: In an organization, provision for taxation as of 31st December 2013 was ₹ 16,000, and on 31st December 2014 ₹ 18,000. Provision for taxation of ₹ 19,000 was made during the year 2014. The tax paid during the year is –
(A) ₹ 17,000
(B) ₹ 19,000
(C) ₹ 2,000
(D) ₹ 16,000
Hint:
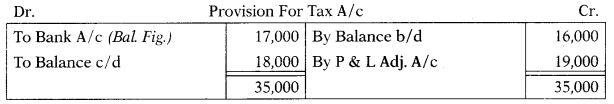
Answer:
(A) ₹ 17,000
Question 10.
Dec 2015: Match the following :
| List-I | List-II |
| P. Cash flow statements | 1. Inflow of funds |
| Q. Inflow of cash | 2. Short-term financial planning |
| R. Investment (maturity period 3 months) | 3. Financing activity |
| S. Payment of dividend | 4. Cash equivalent |
Select the correct answer from the options given below

Answer:
(A)
Question 11.
Dec. 2015:
Statement-I:
In funds flow analysis, current assets and current liabilities are shown separately in a statement of changes in working capital.
Statement-II:
In cash flow analysis, increases and decreases of all current accounts are adjusted in the calculation of cash flow from operating activities.
Select the correct answer from the following
(A) Both statements are correct
(B) Both statements are incorrect
(C) Statement-1 is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
(D) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Answer:
(A) Both statements are correct
Question 12.
Dec. 2015: Match the following:
| List-I | List-II |
| P. Cost accounting | 1. Change in working capital |
| Q. Funds flow statement | 2. Deals with the cost of production, selling & distribution |
| R. Cash How statement | 3. Is an important technique of financial analysis |
| S. Ratio analysis | 4. Cash & cash equivalents |
Select the correct answer from the options given below
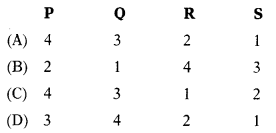
Answer:
(A)
Question 13.
Dec. 2015:
Assertion (A):
A cash flow statement enhances the comparability of the report.
Reason (R):
A cash flow statement eliminates the effect of using different treatments for the same transactions.
Select the correct answer from the following
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(B) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true, but R is false
(D) A is false, but R is true
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Question 14.
Dec. 2015: Arrange the following categories of cash inflows and cash outflows in the correct order of cash flow statements:
(1) Cash flows from investing activities
(2) Cash flows from financing activities
(3) Cash flows from operating activities.
Select the correct answer from the options given below
(A) (3), (1), (2)
(B) (1), (3), (2)
(C) (3), (2), (1)
(D) (2), (1), (3)
Answer:
(A) (3), (1), (2)
Question 15.
Dec. 2015:
Statement-I:
According to AS-3, the provision for taxation should always be treated as a non-operating charge on profits.
Statement-II:
A dividend on shares is an appropriation of profits and not a trading charge.
Select the correct answer from the following
(A) Both statements are correct
(B) Both statements are incorrect
(C) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
(D) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Hint:
Statement I is correct because “provisions for tax” is a non-cash item and always added to net profit to calculate “net prophet before working capital changes”. In the Cash Flow Statement “tax actually paid” is deducted to arrive at “net cash flow from operating activities”.
Statement II is also correct because the dividend is paid on equity share capital or preference share capital te. to the shareholders who are owners of the enterprises and hence it is the appropriation of profit and not a trading charge.
Answer:
(A) Both statements are correct
Question 16.
June 2016: Pride Ltd. has profit after tax ₹ 90,000, depreciation ₹ 17,000, and decrease of debtors ₹ 20,000. The cash generated from operating activities will be:
(A) ₹ 87,000
(B) ₹ 93,000
(C) ₹ 1,27,000
(D) ₹ 53,000
Hint:
| Profit after tax | 90,000 |
| (+) Depreciation (being non-cash item) | 17,000 |
| (+) Decrease in debtors | 20,000 |
| Cash flow from operating activities | 1,27,000 |
Answer:
(C) ₹ 1,27,000
Question 17.
June 2016: The purchase of machinery by issuing long-term notes payable should be reported as a
(A) Non-cash investing and financing activity
(B) Cash outflow in the operating activity
(C) Cash outflow in the investing activity
(D) Cash outflow in the financing activity
Answer:
(A) Non-cash investing and financing activity
Question 18.
June 2016: Which statement contains opening as well as closing balances of cash and cash equivalents and prepared on an accrual basis
(A) Cash flow statement
(B) Fund flow statement
(C) Both (A) and (B) above
(D) Statement of income & expenditure
Answer:
(A) Cash flow statement
Question 19.
Dec. 2016: Income from investments is a cash flow from
(A) Operating activities
(B) Investing activities
(C) Financing activities
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(B) Investing activities
Question 20.
Dec. 2016: A cash flow statement is based upon while fund flow statement recognizes
(A) Cash basis of accounting; accrual basis of accounting
(B) Accrual basis of accounting; the conventional basis of accounting
(C) Mercantile basis of accounting; cash basis of accounting
(D) Cash basis of accounting; cash basis of accounting
Answer:
(A) Cash basis of accounting; accrual basis of accounting
Question 21.
Dec. 2016: Consider the following statements:
(1) Depreciation reduces tax liability; hence it is a source of funds.
(2) Decrease in current liabilities during the year results in an increase in working capital.
(3) The term cash equivalents include short-term marketable investments.
(4) Conversion of debentures into equity shares appears in the fund’s flow statement.
(5) Only non-cash expenses are added to net profit to find out funds from operation.
Select the incorrect statements from the options given below
(A) (1), (3), (4), and (5)
(B) (1), (2), (4), and (5)
(C) (1), (4), and (5)
(D) (2), (3), and (4)
Answer:
(C) (1), (4) and (5)
Question 22.
Dec. 2016: Preference share capital of ₹ 5,00,000 was redeemed at a premium of 10%, partly out of proceeds of the issue of 20,000 equity shares of ₹ 10 each issued at 10% premium and partly out of profits otherwise available for dividends. Choose the correct effect on different activities of cash flow statement from the options given below:
(A) In financing activities, cash out-flow ₹ 5,50,000 and cash inflow ₹ 2,20,000.
(B) In financing activities, cash out-flow ₹ 5,50,000 and in investing activities, cash inflow ₹ 2,20,000
(C) Net ₹ 3,30,000 will be outflow in operating activities
(D) In investing activities cash out-flow of ₹ 5,50,000 and in financing activities cash inflow of ₹ 2,20,000
Answer:
(A) In financing activities, cash out-flow ₹ 5,50,000 and cash inflow ₹ 2,20,000.
Question 23.
2017: In cash flow, income tax paid is treated as:
(A) Operating activity
(B) Investing activity
(C) Financing activity
(D) Not shown anywhere
Answer:
(A) Operating activity
Question 24.
June 2017: By ‘Cash Equivalents’ we mean:
(A) Bank Balance
(B) Short-term highly Liquid Securities
(C) Investments
(D) Investments in debenture
Answer:
(B) Short-term highly Liquid Securities
Question 25.
June 2017: Match the following:
| List I | List II |
| (a) Cash flow statements | (1) Inflow of fund |
| (b) Inflow of cash | (2) Short-term financial planning |
| (c) Investment(maturity period 3 months) | (3) Financing activity |
| (d) Payment of dividend | (4) Cash equivalent |
Codes:

Answer:
(B)
Question 26.
June 2017: Arrange the following categories of cash inflows and cash outflows in the correct order:
(1) Cash from investing activities
(2) Cash from financing activities
(3) Cash from operating activities
Select the correct answer from the options given below
(A) 2, 1 and 3
(B) 1,3 and 2
(C) 3, 2 and 1
(D) 3, 1 and 2
Answer:
(D) 3, 1 and 2
Question 27.
Dec. 2017: In the case of financial enterprises, cash flows arising from____are classified as cash flows from operating activities.
(A) Interest Paid
(B) Interest Received
(C) Dividend Received
(D) All of the above
Answer:
(D) All of the above
Question 28.
Dec. 2017: Some of the account balances of KK Ltd. are as follows in its balance sheet:
| 2016(₹) | 2017(₹) | |
| Share Capital | 2,50,000 | 4,50,000 |
| 10% Debenture | 2,00,000 | 1,50,000 |
| Share Premium | 25,000 | 50,000 |
If the interest paid on debentures was 1 20,000, the net cash flows from financing activities were:
(A) ₹ 1,75,000
(B) ₹ 1,55,000
(C) ₹ 2,05,000
(D) ₹ 2,25,000
Hint:
| Issue of share capital (4,50,000 – 2,50,000) | 2,00,000 |
| Redemption of debentures (1,50,000 – 2,00,000) | (50,000) |
| Securities premium (50,000 – 25,000) | 25,000 |
| Interest paid on debentures | (20,000) |
| Net cash flow from financial activities | 1,55,000 |
Answer:
(B) ₹ 1,55,000
Question 29.
Dec. 2017: Both cash flow statement and fund flow statement are:
(A) Prepared on a cash basis
(B) Prepared on the basis of working capital
(C) Useful for long-term analysis
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(D) None of the above
Question 30.
June 2018: Which of the following involves a movement of cash?
(A) A bonus issue
(B) A right issue
(C) Depreciation of fixed assets
(D) Provision for taxes
Answer:
(B) A right issue
Question 31.
June 2018: The following item would be classified as operating activities in the statement of cash flows:
(A) Acquisition of equipment, payment of dividends
(B) Proceeds from borrowing, payment of interest
(C) Payment of salaries, cash received from the sale of goods
(D) Payments on loan, payments for taxes
Answer:
(C) Payment of salaries, cash received from the sale of goods
Question 32.
June 2018: When the installment paid in respect of a fixed asset acquired on a deferred payment basis includes both interest and loan, the interest element is classified under activities and the loan element is classified under
activities.
(A) Financing, Investing
(B) Investing, Operating
(C) Operating, Financing
(D) Operating, Investing
Answer:
(A) Financing, Investing
Question 33.
June 2018: In the cash flow statement, proceeds from sales of an asset will be considered as:
(A) Investing activity
(B) Financing activity
(C) Operating activity
(D) None of the above
Answer:
(A) Investing activity
Question 34.
June 2018: Which one of the following is false?
(A) If cash outflows exceed cash inflows on an ongoing basis, the business will eventually run out of cash.
(B) Rapidly expanding companies can sometimes face a cash shortage.
(C) Cash is the lifeblood of a business and without it, the business will die.
(D) A profitable company will never run out of cash.
Answer:
(D) A profitable company will never run out of cash.
Question 35.
Dec. 2018: In the case of financial enterprises, cash flow arising from interest and dividends should be classified as cash flow from:
(A) Operating Activities
(B) Financing Activities
(C) Investing Activities
(D) Business Activities
Answer:
(A) Operating Activities
Question 36.
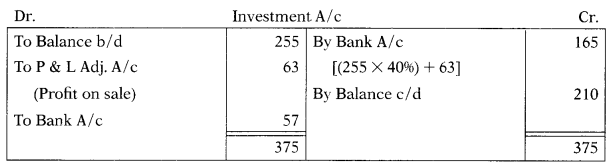
Dec. 2018: Investments at the beginning and at the end of the year 2017-18 were ₹ 255 Lakh and ₹ 210 Lakh respectively. During the year 40 percent of original investments were sold at a profit of ₹ 63 Lakh. Amount of cash inflow and outflow respectively from Investments will be:
(A) ₹ 102 Lakh and ₹ 57 Lakh
(B) ₹ 165 Lakh and ₹ 57 Lakh
(C) ₹ 45 Lakh and Nil
(D) ₹ 147 Lakh and ₹ 39 Lakh
Hint:
Answer:
(B) ₹ 165 Lakh and ₹ 57 Lakh
Question 37.
June 2019: The following information of a non-financial enterprise is given:
Purchase of fixed assets ₹ 40,000;
Proceeds from the sale of equipment ₹ 35,000;
Interest received ₹ 3,000;
Interest paid ₹ 6,000,
Dividend received ₹ 4,000 and
Dividend paid ₹ 15,000.
Amount of cash from investing activities will be –
(A) ₹ 1,000
(B) ₹ (4,000)
(C) ₹ 2,000
(D) ₹ (2,000)
Hint:
– 40,000 + 35,000 + 3,000 + 4,000 = 2,000
Answer:
(C) ₹ 2,000
Question 38.
June 2019: QPR Ltd. has the following balances:
Investment at the end of the year 20172018 ₹ 85,000, Investment at the end of the year 2018-2019 ₹ 70,000. During the year the company had sold 40% of its original investment at a profit of 50%. What will be the amount of cash inflow and cash outflow from the investment:
(A) ₹ 51,000 and ₹ 36,000
(B) ₹ 51,000 and ₹ 19,000
(C) ₹ 1,21,000 and ₹ 85,000
(D) ₹ 1,21,000 and ₹ 19,000
Hint:
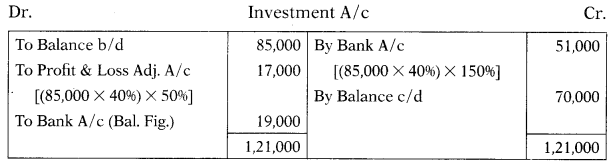
Answer:
(B) ₹ 51,000 and ₹ 19,000
