CA Inter Accounts Question Paper May 2019 – CA Inter Accounts Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
CA Inter May 2019 Accounts Question Paper
Question 1.
(a) M/s First Ltd. began construction of a new factory building on 1st April, 2017. It obtained ₹ 2,00,000 as a special loan to finance the construction of the factory building on 1st April, 2017 at an interest rate of 8% per annum. Further, expenditure on construction of the factory building was financed through other non-specific loans. Details of other outstanding non-specific loans were:
| Amount (₹) | Rate of Interest per annum |
| 4,00,000 | 9% |
| 5,00,000 | 12% |
| 3,00,000 | 14% |
The expenditures that were made on the factory building construction were as follows:
| Date | Amount (₹) |
| 1st April, 2017 | 3,00,000 |
| 31st May, 2017 | 2,40,000 |
| 1st August, 2017 | 4,00,000 |
| 31st December, 2017 | 3,60,000 |
The construction of factory building was completed by 31st March, 2018. As per the provisions of AS-16, you are required to:
(1) Calculate the amount of interest to be capitalized.
(2) Pass Journal entry for capitalizing the cost and borrowing cost in respect of the factory building. (5 Marks)
Answer:
(i) Computation of average accumulated expenses:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| ₹ 3,00,000 × 12/12 | 3,00,000 |
| ₹ 2,40,000 × 10/12 | 2,00,000 |
| ₹ 4,00,000 × 8/12 | 2,66,667 |
| ₹ 3,60,000 × 3/12 | 90,000 |
| 8,56,667 |
![]()
(ii) Computation of average interest rate:
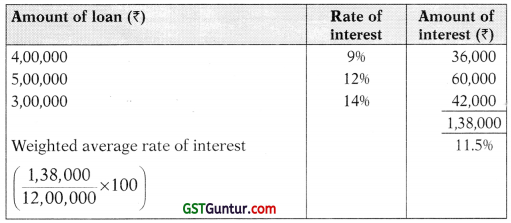
(iii) Interest to be capitalized:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Interest on average accumulated expenses: Specific borrowings (₹ 2,00,000 x 8%) Non-specific borrowings (₹ 6,56,667 × ₹ 11.5%) Amount of interest to be capitalized | 16,000
75,517 |
| 91,517 |
#(₹ 8,56,667 – ₹ 2,00,000)
(iv) Amount to be capitalized for building:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Cost of building ₹ (3,00,000 + 2,40,000 + 4,00,000 + 3,60,000) | 13,00,000 |
| Add: Amount of interest to be capitalized | 91,517 |
| 13,91,517 |
(v) Journal Entry:

(b) On 15th June, 2018, Y limited wants to re-classify its investments in accordance with AS 13 (revised). Decide and state the amount of transfer, based on the following information:
(1) A portion of long-term investments purchased on 1st March, 2017 are to be re-classified as current investments. The original cost of these investments was ₹ 14 lakhs but had been written down by ₹ 2 lakhs (to recognize ‘other than temporary’ decline in value). The market value of these investments on 15th June, 2018 was ₹ 11 lakhs.
(2) Another portion of long-term investments purchased on 15th January, 2017 are to be re-classified as current investments. The original cost of these investments was ₹ 7 lakhs but had been written down to ₹ 5 lakhs (to recognize ‘other than temporary’ decline in value). The fair value of these investments on 15th June, 2018 was ₹ 4.5 lakhs.
(3) A portion of current investments purchased on 15th March, 2018 for 17 lakhs are to be re-classified as long-term investments, as the company has decided to retain them. The market value of these investments on 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 6 lakhs and fair value on 15th June, 2018 was ₹ 8.5 lakhs.
(4) Another portion of current investments purchased on 7th December, 2017 for ₹ 4 lakhs are to be re-classified as long term investments. The market value of these investments was:
on 31st March, 2018 on 15th June, 2018
Answer:
Where long-term investments are reclassified as current investments, transfers
are made at the lower of cost and carrying amount at the date of transfer; and where investments are reclassified from current to long term, transfers are made at lower of cost and fair value on the date of transfer.
Accordingly, the re-classification will be done on the following basis:
| Case | Analysis | Remarks |
| (i) | Carrying amount of investment on the date of transfer is less than the cost. | It will be re-classified as current investment and should be carried at ₹ 12 lakhs in the books. |
| (ii) | Carrying amount of investment on the date of transfer is less than the cost. | It will be re-classified as current investment and should be carried at ₹ 5 lakhs in the books. |
| (iii) | Cost is less than its fair value of ₹ 8.5 lakhs on the date of transfer. | Reclassification of current investment into long-term investments will be made at ₹ 7 lakhs. |
| (iv) | Market value (considered as fair value) is ₹ 3.8 lakhs on the date of transfer which is lower than the cost of 14 lakhs. | Reclassification of current investment into long-term investments will be made at ₹ 3.8 lakhs. |
![]()
(c) State whether the following statements are ‘True’ or ‘False’. Also give reason for your answer:
- As per the provisions of AS-5, extraordinary items should not be disclosed in the statement of profit and loss as a part of net profit or loss for the period.
- As per the provisions of AS-12, government grants in the nature of promoters’ contribution which become refundable should be reduced from the capital reserve.
- As per the provisions of AS-2, inventories should be valued at the lower of cost and selling price.
- As per the provisions of AS-13, a current investments is an investment that is by its nature is readily realizable and is intended to be held for not more than six months from the date on which such investment is made.
- As per the provisions of AS-4, a contingency is a condition or situation, the ultimate outcome of which (gain or loss) will be known or determined only on the occurrence of one or more uncertain future events. (5 Marks)
Answer:
| Sl. No. | True or False | Reason |
| 1. | False | The nature and the amount of each extraordinary item should be separately disclosed in the statement of profit and loss in a manner that its impact on current profit or loss can be perceived. |
| 2. | True | When grants in the nature of promoters’ contribution becomes refundable, in part or in full to the government on non-fulfilment of some specified conditions, the relevant amount refundable to the government is reduced from the capital reserve. |
| 3. | False | Inventories should be valued at the lower of cost and net realizable value (not selling price) as per AS 2. |
| 4. | False | A current investment is an investment that is by its nature readily realizable and is intended to be held for not more than one year from the date on which such investment is made. |
| 5. | False | A contingency is a condition or situation, the ultimate outcome of which, gain or loss, will be known or determined only on the occurrence, or non-occurrence, of one or more uncertain future events. |
(d) The financial statements of PQ Ltd. for the year 2017-18 approved by the Board of Directors on 15th July, 2018. The following information was provided:
- A suit against the company’s advertisement was filed by a party on 20th April, 2018, claiming damages of ₹ 25 lakhs.
- The terms and conditions for acquisition of business of another company have been decided by March, 2018. But the financial resources were arranged in April, 2018 and amount invested was ₹ 50 lakhs.
- Theft of cash of ₹ 5 lakhs by the cashier on 31st March, 2018 but was detected on 16th July, 2018.
- Company sends proposal to sell an immovable property for ₹ 40 lakhs in March, 2018. The book value of the property is ₹ 30 lakhs on 31 st March, 2018. However, the deed was registered on 15th April, 2018.
- A major fire has damaged the assets in a factory on 5th April, 2018. However, the assets are fully insured.
With reference to AS-4 “Contingencies and events occurring after the balance sheet date”, state whether the abovementioned events will be treated as contingencies, adjusting events or non-adjusting events occurring after the balance sheet date. (5 Marks)
Answer:
| Point No. | Analysis | Conclusion |
| (i) | Suit filed against the company is a contingent liability but it was not existing as on balance sheet date as the suit was filed on 20th April after the balance Sheet date. As per AS 4, ‘Contingencies’ used in the Standard is restricted to conditions or situations at the balance sheet date, the financial effect of which is to be determined by future events which may or may not occur. | It will have no effect on financial statements and will be a non-adjusting event. |
| (ii) | Terms and conditions for acquisition of business were finalized and carried out before the closure of the books of account but transaction for payment of financial resources was affected in April, 2018. This is clearly an event occurring after the balance sheet date. | Necessary adjustment to assets and liabilities for acquisition of business is necessary in the financial statements for the year ended 31st March 2018. |
| (iii) | Only those significant events which occur between the balance sheet date and the date on which the financial statements are approved, may indicate the need for adjustment to assets and liabilities existing on the balance sheet date or may require disclosure. In the given case, theft of cash was detected on 16th July, 2018 after approval of financial statements by the Board of Directors. | No treatment is required. |
| (iv) | Adjustments to assets and liabilities are not appropriate for events occurring after the balance sheet date, if such events do not relate to conditions existing at the balance sheet date. In the given case, sale of immovable property was under proposal stage (negotiations also not started) on the balance sheet date. | No adjustment to assets for sale of immovable property is required in the financial statements for the year ended 31st March, 2018. |
| (v) | The condition of fire occurrence was not existing on the balance sheet date. | Only the disclosure regarding event of fire and loss being completely insured may be given in the report of approving authority. |
Question 2.
(a). M/s Amar bought six scooters from M/s Bhanu on 1st April, 2015 on the following terms:
Down payment ₹ 3,00,000
1st instalment payable at the end of 1st year ₹ 1,59,000
2nd instalment payable at the end of 2nd year ₹ 1,47,000
3rd instalment payable at the end of 3rd year ₹ 1,65,000
Interest is charged at the rate of 10% per annum.
M/s Amar provides depreciation @ 20% per annum on the diminishing balance method.
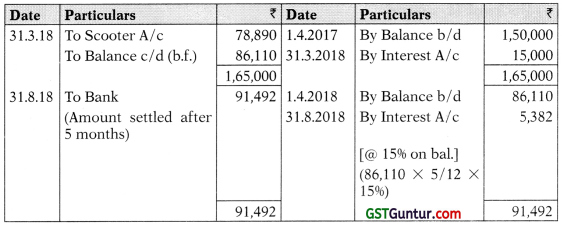
On 31 st March, 2018 M/s Amar failed to pay the 3rd instalment upon which M/s Bhanu repossessed two Scooters. M/s Bhanu agreed to leave the other four Scooters with M/s Amar and adjusted the value of the repossessed Scooters against the amount due. The Scooters taken over were valued on the basis of 30% depreciation per annum on written down value. The balance amount remaining in the vendor’s account after the above adjustment was paid by M/s Amar after 5 months with interest @15% per annum.
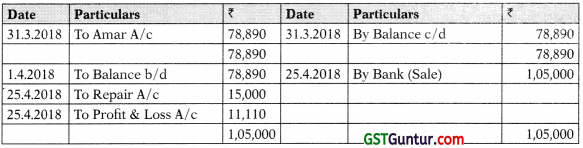
M/s Bhanu incurred repairing expenses of ₹ 15,000 on repossessed scooters and sold scooters for ₹ 1,05,000 on 25th April, 2018.
You are required to:
(1) Calculate the cash price of the Scooters and the interest paid with each instalment.
(2) Prepare Scooters Account and M/s Bhanu Account in the books of M/s Amar.
(3) Prepare Goods Repossessed Account in the books of M/s Bhanu. (10 Marks)
Answer:
(i) Calculation of Interest and Cash Price
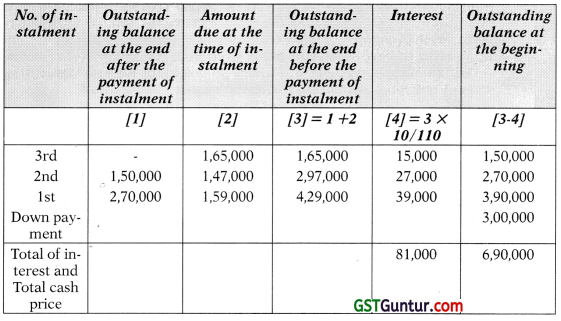
(ii) Books of M/s Amar
Scooters A/c
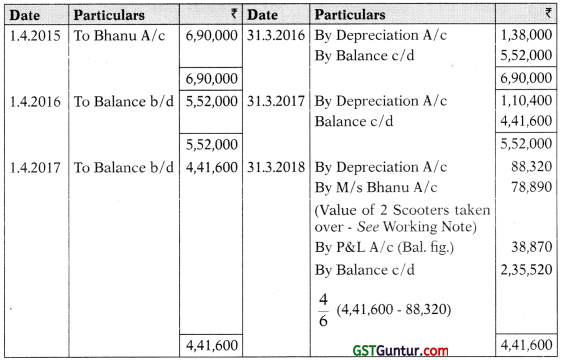
Working Note:
Value of Scooters taken over:

(iii) M/s Bhanu A/c
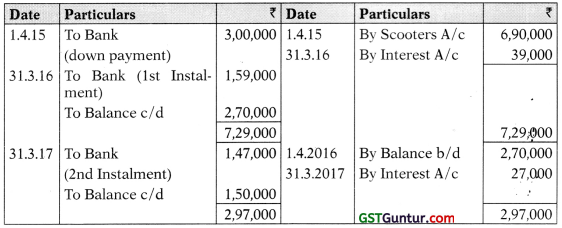
(iv) In the Books of M/s Bhanu
Goods Repossessed A/c
![]()
(b) A fire occurred in the premises of M/s Bright on 25th May, 2017. As a result of fire, sales adversely affected up to 30th September, 2017. The firm had taken Loss of profit policy (with and average clause) for ₹ 3,50,000 having indemnity period of 5 months.
There is an upward trend of 10% in sales.
The firm incurred an additional expenditure of ₹ 30,000 to maintain the sales. There was a saving of ₹ 5,000 in the insured standing charges.
| Actual turnover from 25th May, 2017 to 30th September, 2017 | ₹ 1,75,000 |
| Turnover from 25th May, 2016 to 30th September, 2016 | ₹ 6,00,000 |
| Net profit for last financial year | ₹ 2,00,000 |
| Insured standing charges for the last financial year | ₹ 1,75,000 |
| Total standing charges for the last financial year | ₹ 3,00,000 |
| Turnover for the last financial year | ₹ 15,00,000 |
| Turnover for one year from 25th May, 2016 to 24th May, 2017 | ₹ 14,00,000 |
You are required to calculate the loss of profit claim amount, assuming that entire sales during the interrupted period was due to additional expenses. (10 Marks)
Answer:
Computation of the amount of claim for loss of profit:
1.

2. Calculation of loss of Profit
Gross Profit on reduction in turnover @ 25% on ₹ 4,85,000 1,21,250
(see working note 1)
Add: Additional Expenses
Lower of:
(i) Actual = ₹ 30,000
(ii)
![]()
30,000 × [3,85,000/(3,85,000 + 1,25,000)] = ₹ 22,647
(iii) G.P. on sales generated bv additional expenses
175000 × 25% = ₹ 43,750
It is given that entire sales during the interrupted period was due to additional expenses.
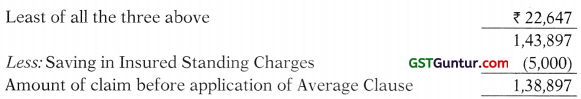
3. Application of Average Clause:
![]()
(3,50,000/3,85,000) × 1,38,897 = ₹ 1,26,270
Amount of claim under the policy = ₹ 1,26,270
Working Notes:
1.
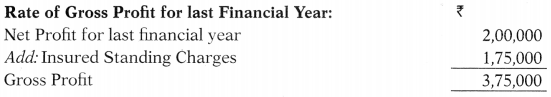
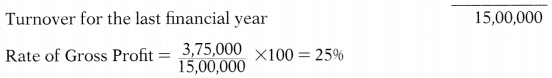
2. Annual Turnover (adjusted):

Question 3.
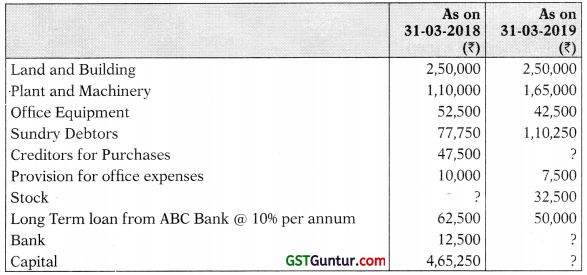
(a) The following balances appeared in the books of M/s Sunshine Traders:
Other information was as follows:
- Depreciation to be provided as follows:
Land and Machinery 5% per annum
Plant and Machinery 10% per annum
Office Equipment 15% per annum - On 01.10.2018 the firm sold machine having Book Value ₹ 20,000 (as on 31.03.2018) at a loss of ₹ 7,500. Now machine was purchases on 01.01.2019.
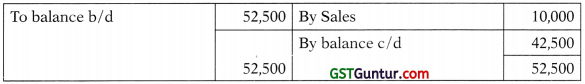
- Office equipment was sold at its book value on 01.04.2018.
- Loan was partly repaid on 31.03.2019 together with interest for the year.
You are required to prepare:
- Trading and Profit & Loss account for the year ended 31st March, 2019.
- Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2019. (12 Marks)
Answer:
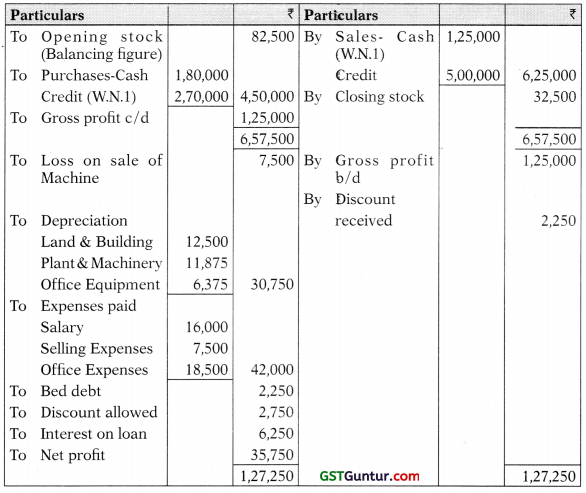
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c for the year ended 31.3.2019
Balance Sheet as on 31-3-2019
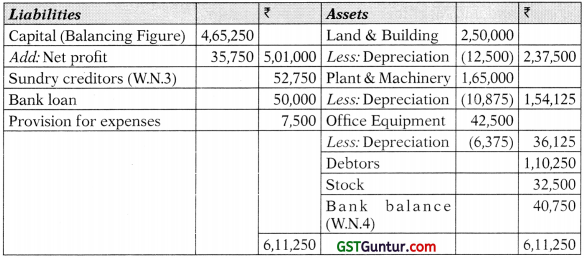
Working Notes:
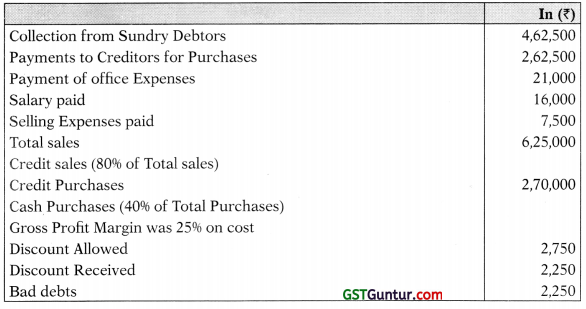
1. Computation of Sales and Purchases:
Total sales = ₹ 6,25,000
Cash sales = 20% of total sales (6,25,000) = ₹ 1,25,000
Credit sales = 80% of total sales = (6,25,000) = ₹ 5,00,000
Gross Profit 25% on cost = 6,25,000 × \(\frac{25}{125}\) = ₹ 1,25,000
Credit purchases = ₹ 2,70,000
Credit purchases = 60% of total purchases
Cash purchases = 40% of total purchases
Total purchases = \(\frac{2,70,000}{60}\) × 100 = ₹ 4,50,000
Cash purchases = 4,50,000 – 2,70,000 = ₹ 1,80,000
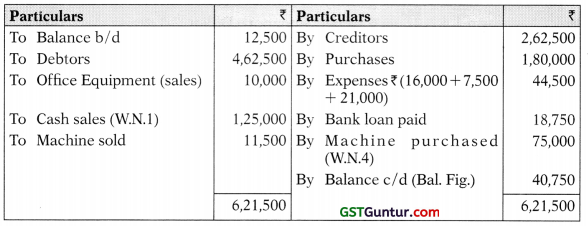
2. Plant & Machinery A/c
| Particulars | ₹ | Particulars | |
| To Balance b/d | 1,10,000 | By Sale of Machinery A/c | 20,000 |
| To Cash-purchase (Bal. Fig.) | 75,000 | By Balance c/d | 1,65,000 |
| 1,85,000 | 1,85,000 |
Depreciation on Plant & Machinery:
| @ 10% p.a. on ₹ 20,000 for 6 months = | 1,000 |
| @ 10% p.a. on ₹ 90,000 (i.e. ₹ 1,10,000 – ₹ 20,000) = | 9,000 |
| @ 10% p.a. on ₹ 75,000 for 3 months (i.e. during the year) = | 1,875 |
| 11,875 | |
Sale of Machinery A/c
| Particulars | | Particulars | ₹ |
| To Plant and Machinery | 20,000 | By Depreciation (20,000 X 10% X 1/2) | 1000 |
| By P&L A/c | 7,500 | ||
| By Bank (Balancing figure) | 11,500 | ||
| 20,000 | 20,000 |
![]()
3. Creditors Account
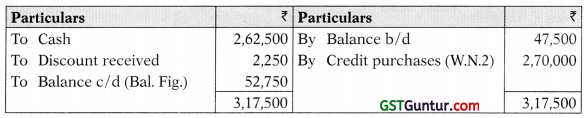
Debtors A/c
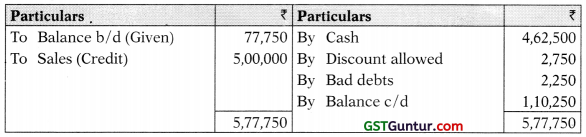
Provision for Office Expenses A/c
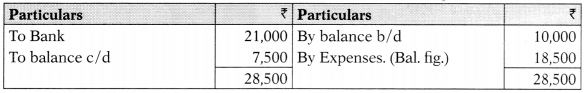
4. Bank A/c
5. Office Equipment A/c
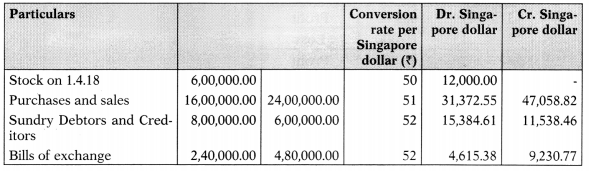
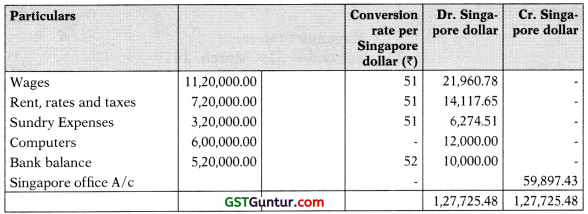
(b) M/s Rani & Co. has head office at Singapore and branch at Delhi (India). Delhi branch is an integral foreign operation of M/s Rani & Co., Delhi branch furnishes you with its Trial Balance as on 31st March, 2019 and the additional information thereafter.
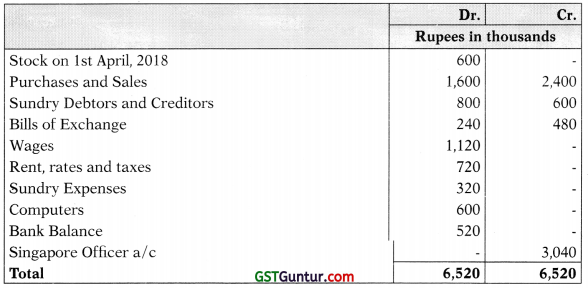
Additional information:
(a) Computers were acquired from a remittance of Singapore dollar 12,000 received from Singapore Head Office and paid to the suppliers. Depreciate Computers at the rate of 40% for the year.
(b) Closing Stock of Delhi branch was ₹ 15,60,000 on 31st March, 2019.
(c) The Rates of Exchange may be taken as follows:
- on 1.4.2018 @ ₹ 50 per Singapore Dollar
- on 31.3.2019 @ ₹ 52 per Singapore Dollar
- average Exchange Rate for the year @ ₹ 51 per Singapore Dollar
- conversion in Singapore Dollar shall be made upto two decimal accuracy.
(d) Delhi Branch Account showed a debit balance of Singapore Dollar 59,897.43 on 31.3.2019 in the Head Office books and there were no items pending for reconciliation.
In the books of Head office, you are required to prepare:
- Revenue statement for the year ended 31st March, 2019. (in Singapore Dollar)
- Balance Sheet as on that date, (in Singapore Dollar) (8 Marks)
Answer:
Revenue Statement for the year ended 31st March, 2019
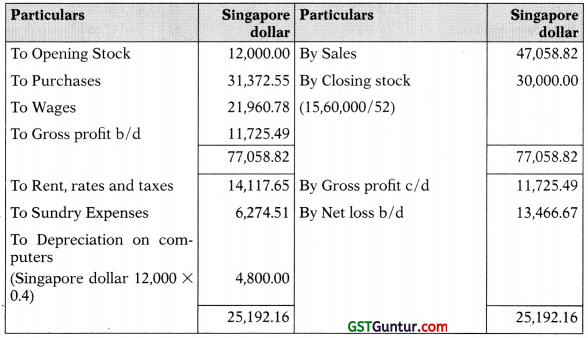
Balance Sheet of Delhi Branch as on 31st March, 2019
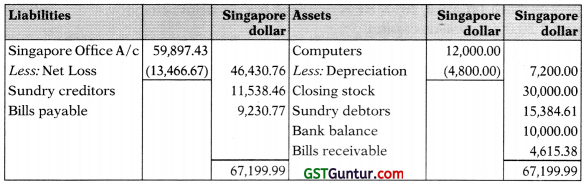
Working Note:
Delhi Branch Trial Balance in (Singapore $) as on 31st March, 2019
![]()
Question 4.
The following is the Balance Sheet of M/s Red and Black as on 31st March, 2018:
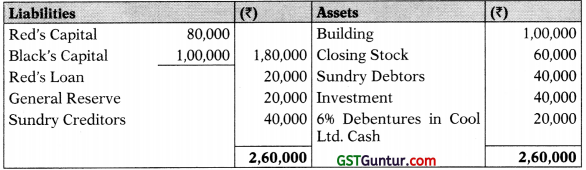
It was agreed that Mr. White is to be admitted for a fifth share in the future profits from 1st April, 2018. He is required to contribute cash towards goodwill and ₹ 20,000 towards capital.
(a) The following further information is furnished:
(i) The partners Red and Black shared the profits in the ratio of 3:2.
(ii) Mr. Red was receiving a salary of ₹ 1000 p.m. from the very inception of the firm in addition to the share of profit.
(iii) The future profit ratio between Red, Black and White will be 3:1:1. Mr. Red will not get any salary after the admission of Mr. White.
(iv) The goodwill of the firm should be determined on the basis of 2 years’ purchase of the average profits from business of the last 5 years. The particulars of profits/losses are as under:
| Year Ended | (₹) | Profit/Loss |
| 31.3.2014 | 40,000 | Profit |
| 31.3.2015 | 20,000 | Loss |
| 31.3.2016 | 40,000 | Profit |
| 31.3.2017 | 50,000 | Profit |
| 31.3.2018 | 60,000 | Profit |
The above profits and losses are after charging the salary of Mr. Red. The profit of the year ended 31st March, 2014included an extraneous profit of ₹ 60,000 and the loss of the year ended 31st March, 2015 was on account of loss by strike to the extent of ₹ 40,000.
(v) It was agreed that the value of the goodwill should not appear in the book of the firm.
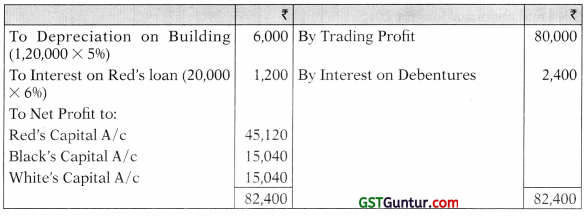
(b) Trading profit for the year ended 31st March, 2019 was ₹ 80,000 (Before charging depreciation).
(c) Each partner had drawn ₹ 2,000 per month as drawing during the year 2018-19.
(d) On 31st March, 2019 the following balances appeared in the books:
Building (Before Depreciation) ₹ 1,20,000
Closing Stock ₹ 80,000
Sundry Debtors NIL
Sundry Creditors NIL
Investment ₹ 40,000
(e) Interest @ 6% per annum on Red’s loan was not paid during the year.
(f) Interest on Debenture received during the year.
(g) Depreciation is to be provided @ 5% on Closing Balance of Building.
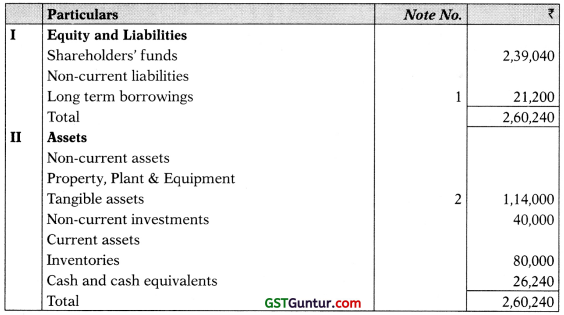
(h) Partners applied for conversion of the firm into a private Limited Company, i.e. RBW Private Limited. Certificate received on 1.4.2019.
They decided to convert Capital accounts of the partners into share capital, in the ratio of 3:1:1 (on the basis of total Capital as on 31.3.2019). If necessary, partners have to subscribe to fresh capital or withdraw.
You are required to prepare:
- Profit & Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2019 in the books of M/s Red and Black.
- Balance Sheet as on 1st April, 2019 in the books of RBW Private Limited. (20 Marks)
Answer:
Statement of Profit & Loss for the year ended on 31st March, 2019
Balance Sheet of the RBW Pvt. Ltd. as on 1-4-2019
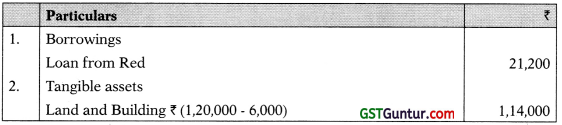
Notes to Accounts:
Working Notes:
1. Computation of goodwill:
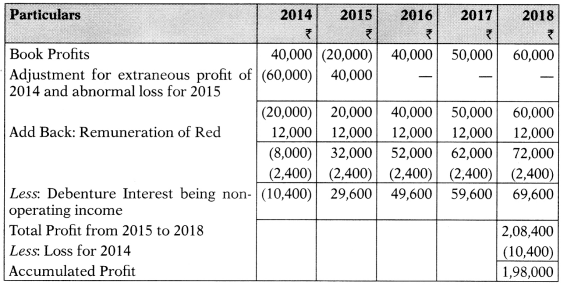

2. Partners’ Capital Accounts
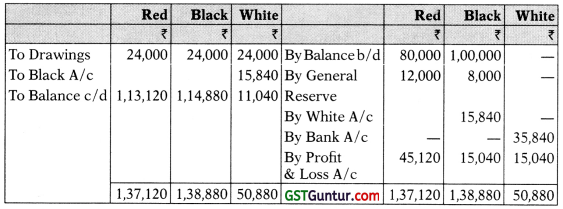
3. Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2019
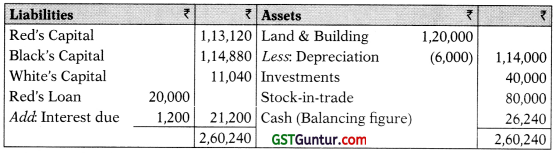
![]()
4. Conversion into Company
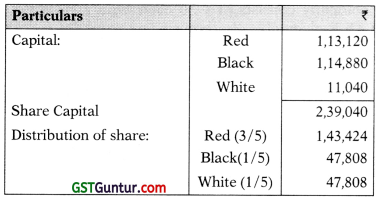
Red should subscribe shares of ₹ 30,304 (₹ 1,43,424 – ₹ 1,13,120) and White should subscribe shares of ₹ 36,768 (₹ 47,808 less 11,040). Black withdraws ₹ 67,072 (₹ 47,808 – ₹ 1,14,880).
5. Adjustment for Goodwill:

Question 5.
(a) The Summarized Balance Sheet of Clean Ltd. as on 2019 is as follows: 31st March,
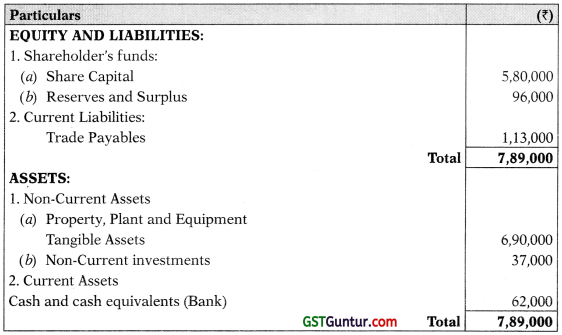
The Share Capital of the company consists of ₹ 50 each Equity shares of ₹ 4,50,000 and ₹ 100 each 8% Redeemable Preference Shares of ₹ 1,30,000 (issued on 1.4.2017)
Reserves and Surplus comprises statement of profit and loss only.
In order to facilitate the redemption of preference shares at a premium of 10%, the Company decided:
(a) to sell all the investments for ₹ 30,000.
(b) to finance part of redemption from company funds, subject to, leaving a Bank balance of ₹ 24,000.
(c) to issue minimum equity share of ₹ 50 each at a premium of ₹ 10 per share to raise the balance of funds required.
You are required to
- Pass Journal Entries to record the above transactions.
- Prepare Balance Sheet as on completion of the above transactions. (10 Marks)
Answer:
Journal Entries
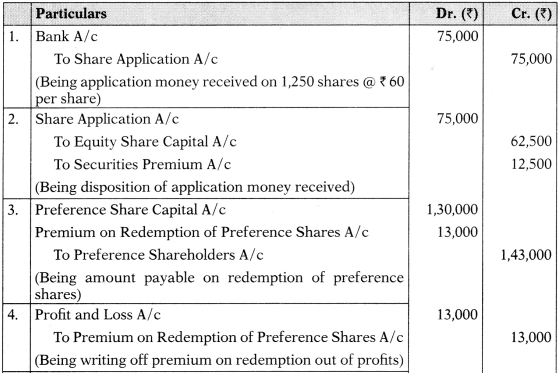
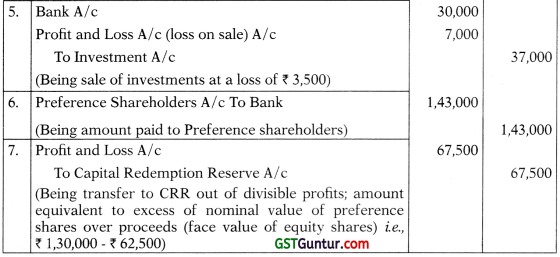
Balance Sheet of Clean Ltd. (after redemption)

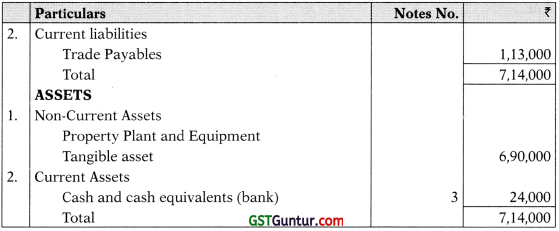
Notes to accounts:
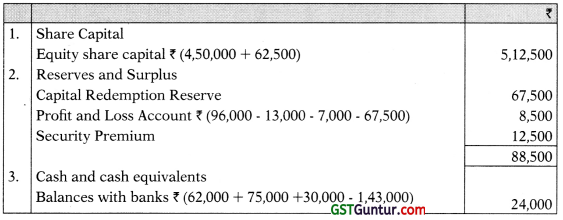
Working Note:

(b) The following information was provided by M/s PQR Ltd. for the year ended 31st March, 2019:
- Gross Profit Ratio was 25% for the year, it amounts to ₹ 3,75,000.
- Company sold goods for cash only.
- Opening inventory was lesser than closing inventory by ₹ 25,000.
- Wages paid during the year ₹ 5,55,000.
- Office expenses paid during the year ₹ 35,000.
- Selling expenses paid during the year ₹ 15,000.
- Dividend paid during the year ₹ 40,000 (including dividend distribution tax).
- Bank Loan repaid during the year ₹ 2,05,000 (included interest ₹ 5,000)
- Trade payable on 31st March, 2018, were ₹ 50,000 and on 31st March, 2019 were ₹ 35,000.
- Amount paid to Trade payables during the year ₹ 6,10,000
- Income Tax paid during the year amounts to ₹ 55,000 (Provision for taxation as on 31st March, 2019, ₹ 30,000)
- Investments of ₹ 8,20,000 sold during the year at a profit of ₹ 20,000.
- Depreciation on furniture amounts to ₹ 40,000.
- Depreciation on other tangible assets amounts to ₹ 20,000.
- Plant and Machinery purchased on 15th November, 2018 for 13,50,000.
- On 31st March, 2019 ₹ 2,00,000, 1% Debentures issued at face value in an exchange for a plant.
- Cash and Cash equivalents on 31st March, 2018, ₹ 2,25,000.
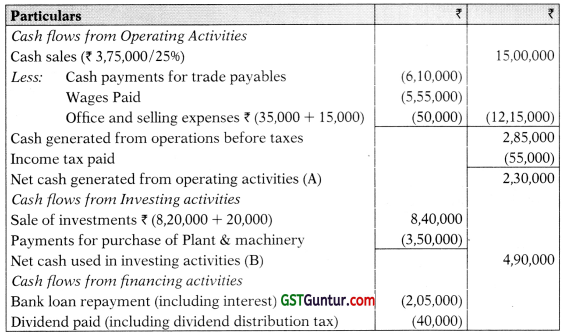
(A) Prepare cash flow statement for the year ended 31 st March, 2019, using direct method.
(B) Calculate cash flow from operating activities, using indirect method. (10 Marks)
Answer:
(i)
Cash Flow Statement for the year ended 31st March, 2019
(Using direct method)

![]()
(ii) ‘Cash Flow from Operating Activities’ by indirect method:
| Particulars | ₹ | |
| Net Profit for the year before tax and extraordinary items | 2,80,000 | |
| Add. Non-Cash and Non-Operating Expenses: | ||
| Depreciation | 60,000 | |
| Interest Paid | 5,000 | |
| Less: Non-Cash and Non-Operating Incomes: | ||
| Profit on Sale of Investments | (20,000) | |
| Net Profit after Adjustment for Non-Cash Items | 15,000 | 3,25,000 |
| Less: Decrease in trade payables | 25,000 | |
| Increase in inventory | (40,000) | |
| Cash generated from operations before taxes | 2,85,000 |
Working Note:
Computation of net profit earned during the year:

Question 6.
Answer any four of the following : (5 Marks)
(a) Write short note on Timing difference and permanent Difference as per AS 22. “
Answer:
Matching of taxes against revenue for a period poses special problems arising from the fact that in number of cases, taxable income maybe different from the accounting income.
The divergence between taxable income may be different from the accounting income arises due to two main reasons:
- There are differences between items of revenue and expenses as appearing in the statement of profit and loss and the items which are considered as revenue, expenses or deductions for tax purposes, known as Permanent Difference.
- There are differences between the amount in respect of a particular item of revenue or expense as recognized in the statement of profit and loss and the corresponding amount which is recognized for the computation of taxable income, known as Timing Difference.
Permanent differences are the differences between taxable income and accounting income which arise in one accounting period and do not reverse subsequently.
For example, an income, exempt from tax or an expense that is not allowable as a deduction for tax purposes.
Timing differences are those differences between taxable income and accounting income which arise in one accounting period and are capable of reversal in one or more subsequent periods.
For e.g., Depreciation, Bonus, etc.
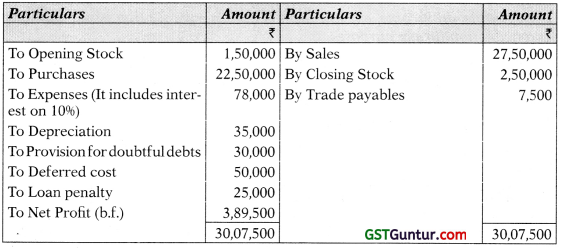
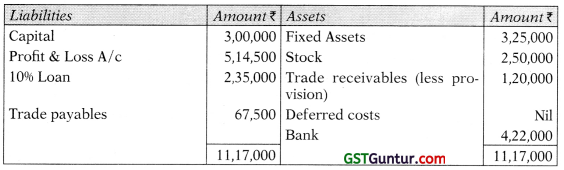
(b) Summarized Balance Sheet of Cloth Trader as on 31.03.2017 is given below:
| Liabilities | Amount (₹) | Assets | Amount (₹) |
| Proprietor’s Capital | 3,00,000 | Fixed Assets | 3,60,000 |
| Profit & Loss Account | 1,25,000 | Closing Stock | 1,50,000 |
| 10% Loan Account | 2,10,000 | Sundry Debtors | 1,00,000 |
| Sundry Creditors | 50,000 | Deferred Expenses | 50,000 |
| Cash & Bank | 25,000 | ||
| 6,85,000 | 6,85,000 |
Additional Information is as follows:
- The remaining life of fixed assets is 8 years. The pattern of use of the asset is even. The net realizable value of fixed assets on 31.03.2018 was ₹ 3,215,000.
- Purchases and Sales in 2017-18 amounted to ₹ 22,50,000 and ₹ 27,50,000 respectively.
- The cost and net realizable value of stock on 31.03.2018 were ₹ 2,00,000 and ₹ 2,50,000 respectively.
- Expenses for the year amounted to ₹ 78,000.
- Deferred Expenses are amortized equally over 5 years.
- Sundry Debtors on 31.03.2018 are ₹ 1,50,000 of which ₹ 5,000 is doubtful. Collection of another ₹ 25,000 depends on successfully re-installation of certain product supplied to the customer.
- Closing Sundry Creditors are ₹ 75,000, likely to be settled at 10% discount.
- Cash balance as on 31.03.2018 is ₹ 4,22,000.
- There is an early repayment penalty for the loan of ₹ 25,000.
You are required to prepare:
(Not assuming going concern)
- Profit & Loss Account for the year 2017-18.
- Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2018. (5 Marks)
Answer:
Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 2017-18
(Not assuming going concern)
Balance Sheet as at 31st March, 2018 (Not assuming going concern)
(c) Tarun Ltd. was incorporated on 1 st July, 2018 to acquire a running business of Vinav Sons with effect from 1st April, 2018. During the year 2019-18, the total sales were ₹ 12,00,000 of which ₹ 2,40,000 were for the first six months. The Gross Profit for the year is ₹ 4,15,000. The expenses debited to the Profit and Loss account included:
- Director’s fees ₹ 25,000
- Bad Debts ₹ 6,500
- Advertising ₹ 18,000
(under a contract amounting to ₹ 1,500 per month) - Company Audit Fees ₹ 15,000
- Tax Audit Fees ₹ 10,000
(1) Prepare a statement showing pre-incorporation and post-incor-poration profit for the year ended 31st March, 2019.
(2) Explain how profit are to be treated. (5 Marks)
Answer:
Statement showing the computation of Profits for the pre-incorporation and post- incorporation periods for the year ended 31st March, 2019
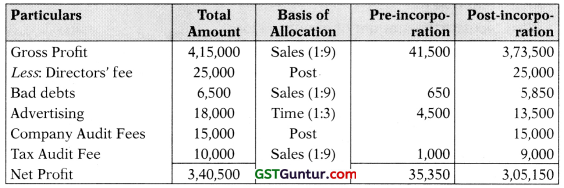
Pre-incorporation profits to be transferred to capital reserve and post-incor-poration profit to be transferred to profit & Loss A/c.
Working Notes:
(i) Computation of Sales ratio:
| Particulars | ₹ |
| Sales for period up to 30.06.2018 (2,40,000 × 3/6)
Sales for period from 01.07.2018 to 31.03.2019 (12,00,000 – 1,20,000) |
1,20,000
10,80,000 |
Thus, Sales Ratio = 1:9 (1,20,000: 10,80,000)
(ii) Computation of Time ratio:
1st April, 2018 to 30th June, 2018: 1st July, 2018 to 31st March, 2019
= 3 months : 9 months = 1 : 3
Thus, Time Ratio is 1 : 3
(d) State the circumstances when Garner vs. Murray rule is not applicable. (5 Marks)
Answer:
Garner vs. Murray rule is non-applicable in the following cases:
- When the solvent partner has a debit balance in the capital account. Only solvent partners will bear the loss of capital deficiency of insolvent partner in their capital ratio. If incidentally a solvent partner has a debit balance in his capital account, he will escape the liability to bear the loss due to insolvency of another partner.
- When the firm has only two partners.
- When there is an agreement between the partners to share the deficiency in capital account of insolvent partner.
- When all the partners of the firm are insolvent.
(e) Wooden Plywood Limited has a normal wastage of 5% in the production process. During the year 2017-18, the Company used 16,000 MT of Raw material costing ₹ 190 per MT. At the end of the year, 950 MT of wastage was in stock. The accountant wants to know how this wastage is to be treated in the books.
You are required to:
- Calculate the amount of abnormal loss.
- Explain the treatment of normal loss and abnormal loss.
[In the context of AS-2- (Revised)] (5 Marks)
Answer:
(i) As per AS 2 (Revised) ‘Valuation of Inventories’, abnormal amounts of wasted materials, labour and other production costs are excluded from cost of inventories and such costs are recognized as expenses in the period in which they are incurred.
The normal loss will be included in determining the cost of inventories (finished goods) at the year end.
Amount of Abnormal Loss:
(ii)
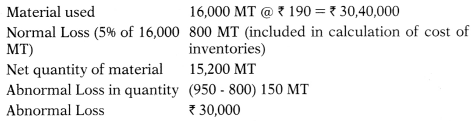
[150 units @ ₹ 200 (₹ 30,40,000/15,200)]
Amount of ₹ 30,000 (Abnormal loss) will be charged to the Profit and Loss statement.