Bills of Exchange – CA Foundation Accounts Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Bills of Exchange – CA Foundation Accounts Study Material
Question 1.
Meaning of Bills of exchange.
Answer:
Meaning of Bills of exchange:
A bill of exchange has been defined as:
- an “instrument in writing
- containing an unconditional order
- signed by the maker/drawer
- directing a certain person (drawee)
- to pay a certain sum of money only
- to a certain person or to the order of a certain person or to the bearer of the instrument”, (payee)
Draft of a Bill of Exchange:
→ When such an order is accepted by writing on the face of the order itself, it becomes a valid bill of exchange.

→ A cheque is a bill of exchange but all bill of exchanges are not cheque.
→ In above bill of exchange ‘A’ is drawer as well as payee and ‘B’ is drawee
![]()
Question 2.
Meaning of Promissory Note.
Answer:
Meaning of Promissory Note:
A Promissory note is:
- an instrument in writing,
- not being a bank note or currency note,
- containing an unconditional undertaking (promise)
- signed by the maker (promisor)
- to pay a certain sum of money only to a certain person or to the order of a certain person.
Under section 31(2) of the Reserve Bank of India Act a promissory note cannot be made payable to bearer except by RBI &/or Central Government.
Draft of a Promissory Note:

Question 3.
Renewal of a bill.
Answer:
Renewal of a bill:
- On the due date, if acceptor is unable to pay the amount of bill, then he can approach the Drawer, for renewal of the bill.
- Renewal means giving further time for the payment of bill.
- For this delay the Drawer will/may collect Interest from acceptor on the delayed amount [total amount (-) amount if any paid at the time of renewal] for delayed/extended period.
- Renewal will involve cancellation of the old bill, accruing the interest and preparing a new bill for balance amount with interest. (Some part amount may be paid immediately)
Model Entry for renewal which can be passed in three parts:
→ Entry for cancellation of the old bill given above is assuming bill was retained.
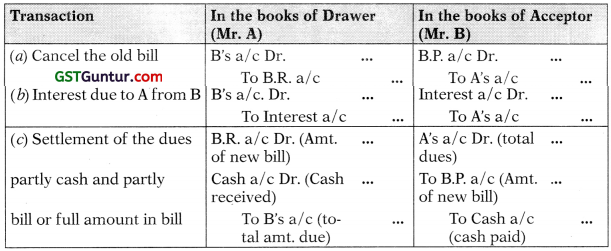
→ Entry for renewal can be passed in any other combination giving same net effect as in above three entries.
![]()
Question 4.
Noting of bill
Answer:
Noting of Bill and Noting charges:
- When a bill is dishonoured the holder of the bill (holder can be drawer, endorsee or Bank) may present it to notary public (A Government appointed Authority).
- Notary public will present the bill to the acceptor of the bill and if he doesn’t pay, the notary public will note the fact of dishonour on the bill.
- This (Noting) becomes a final evidence for court cases.
- The charges charged by notary for this service is called noting charges.
- Noting charges will be paid by the holder of the bill but ultimately it will be recovered from the drawee/acceptor (Party wrhich dishonours the bill).
- Hence, noting charges will be an expense for the drawee (acceptor) of the bill & income for the Notary Public.
Question 5.
Retirement of bill
Answer:
Retirement of the bill:
- Retirement of the bill means that payment is made before the due date.
- Therefore, normally the receiver will allow some rebate/discount to the payer.
- Entry for payment/receipt will be recorded net of rebate.
- Thus retirement is the opposite of renewal. In retirement payment is made early whereas in renewal payment is delayed.
Model entry for retirement of the bill:
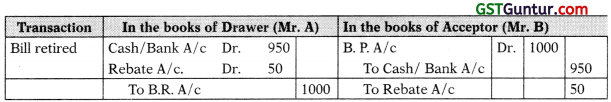
Question 6.
Accommodation Bill.
Answer:
Accommodation Bill:
Accommodation bill is the bill drawn for financial accommodation (help) of one or both the parties. Thus it is not backed by any trade transactions. Parties involved will be related to each other. Either one bill may be drawn or both may draw bill on each other. Such bills are discounted, proceeds are used & on maturity amount is returned to Bank. Alternatively both parties may draw bill on each other & get them discounted respectively.
Meaning & Purpose of Accommodation Bill:
→ Bills of exchange are usually drawn to facilitate trade transactions, that is, bills are meant to finance actual purchase and sale of goods.
→ But the mechanism of bill can be utilized to raise finance also.
→ Therefore, an accommodation bill is one which is drawn, accepted or endorsed for the purpose of arranging financial accommodation for one or more interested parties.
→ It is not a genuine trade bill.
→ Suppose A needs finance for three months. In that case he may persuade his friend B to accept his bill. The bill of exchange may then be taken by A to his bank and discounted there. Thus, A will be able to make use of funds. When the three months period draws to a close A will send the requisite amount to B and B will meet the bill. Thus, A is able to raise money for his use.
→ If both A and B need money, the same device can be used. Either A accepts a bill of exchange or B does. In either case, the bill will be discounted with the bank and the proceeds divided between the two parties according to their needs. The proportionate discount will also be transferred. On the due date the acceptor will receive from the other party of his share. The bill will then be met.
→ When bills are used for such a purpose, these are known as accommodation bills. If bill is dishonoured the first party (i.e. drawer) will have to pay to the Bank.
→ Entries are passed in the books of two parties exactly in the same way as for ordinary bills. The only additional entry to be passed is for sending the remittance to the other party and also for debiting the other party with the requisite amount of discount.
![]()
Question 7.
Bill of Exchange and Promissory Note.
Answer:
Distinction between a Bill of Exchange & a Promissory Note – Important points of comparison are:
→ A promissory note needs no acceptance as required for a bill of exchange, as the debtor himself writes the document promising to pay the stated amount.
→ In case of bill of exchange, the drawer and the payee may be the same person but in case of a promissory note, the maker and the payee cannot be the same person.
→ In case of bill of exchange the drawee and payee cannot be same. But if such situation arises, due to subsequent endorsements then bill will get cancelled. Similarly promissory note will get cancelled if due to endorsement maker/promisor and promisee becomes same, because person liable to pay and person entitled to receive both are same.
→ Both are negotiable instruments, and can be transferred by endorsement.
→ For accounting purposes both will be treated alike & both will be classified as bills payable & bills receivable.
Question 8.
B owes C a sum of ₹ 600/- On 1st April, 2006 he gives promissory note for the amount for 3 months to C who gets it discounted with his bankers for ₹ 590/-. On the due date the bill is dishonoured the bank paying ₹ 5/- as noting charges. B then pays ₹ 200/- in cash and accepts a bill of exchange drawn on him for the balance together with ₹ 10/- as interest. This bill of exchanges is for 2 months and on the due date the bill is again dishonoured, C paying ₹ 5/- for noting charges. Draft the journal entries to be passed in the books of B and C.
Solution:
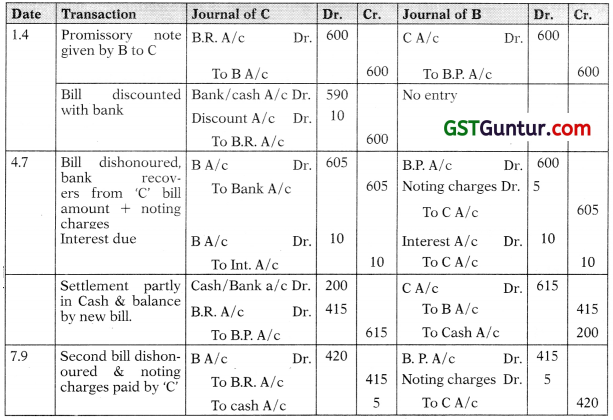
Question 9.
B sends his promissory note for 3 months to C for ₹ 600 on May 1, 2006. C gets it discounted with his bankers at 6 per cent per annum. On the due date the bill is dishonoured, the bank paying ₹ 10 as noting charges. C agrees to accept ₹ 225 in cash ₹ 25 for noting charges and interest) and another promissory note for ₹ 400 for 2 months. On the due date B approaches C again and asks for renewal of the bill for a further period of 3 months. C agrees to the request, provided B pays ₹ 20 as interest in cash. This last bill is paid on maturity. Draft journal entries in the books of B and C.
Solution:
(Renewal of discounted bill & 2nd time renewal):
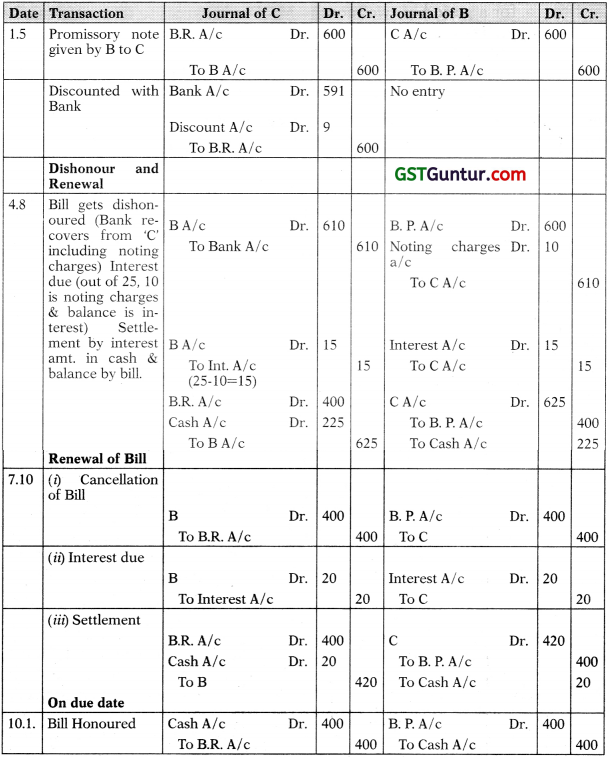
Question 10.
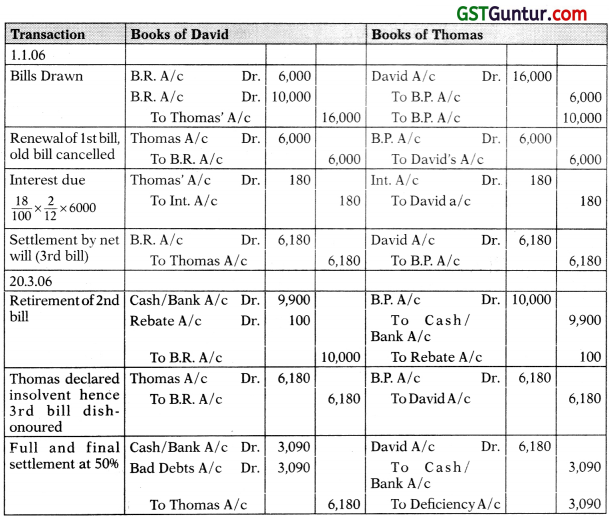
Mr. David draws two bills of exchange on 1-1-2006 for ₹ 6,000 and ₹ 10,000. The bills of exchange for ₹ 6,000 is for two months while the bill of exchange for ₹ 10,000 is for three months. These bills are accepted by Mr. Thomas. On 4-3-2006 Mr. Thomas requests Mr. David to renew the first bill with interest at 18% p.a. for a period of two months. Mr. David agrees to this proposal.
On 20-3-2006 Mr. Thomas retires the acceptance for ₹ 10,000, the interest rebate i.e. discount being ₹ 100. Before the due date of the renewed bill, Mr. Thomas becomes insolvent and only 50 paise in a rupee could be recovered from his estate. You are to give the journal entries in the books of Mr. David.
Solution:
(Renewal & Retirement):
Question 11.
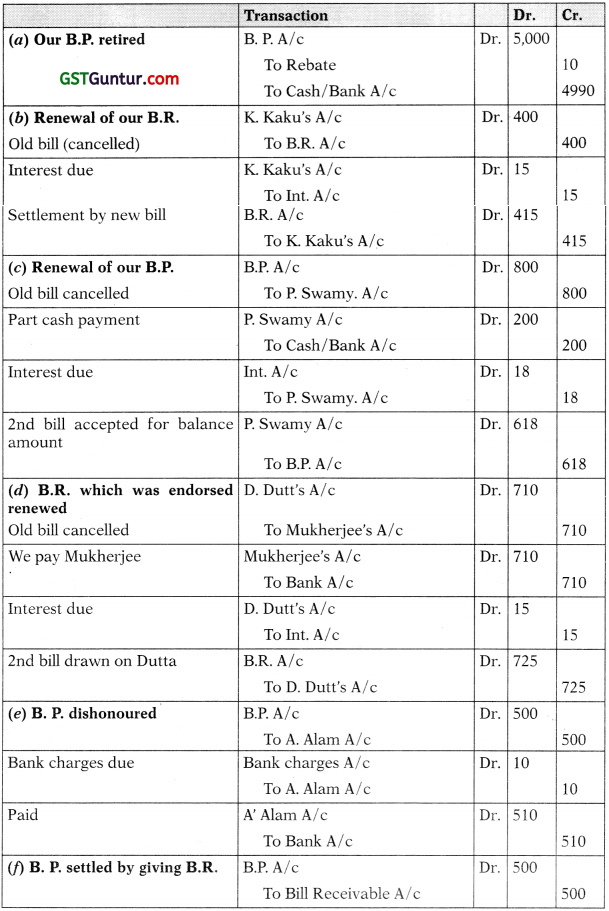
Journalise the following transactions in the books of J. Jaggi:
(a) Our acceptance to M. Madan for ₹ 5,000/- retired before due date, rebate allowed ₹ 10/-.
(b) K. Kaku’s acceptance for ₹ 400/- renewed for a further period of 3 months, interest charged at 15 per cent.
(c) Our acceptance to P. Swamy for ₹ 800/- renewed for 3 months on the condition that ₹ 200/- is paid in cash immediately and the remaining balance to carry interest at 12 per cent.
(d) D. Dutt’s promissory note for ₹ 700/- which we had endorsed in favour of P. Mukherjee dishonoured. P. Mukherjee paid ₹ 10/- as noting charges. We pay P. Mukherjee by cheque and accept from D. Dutt another bill for the amount due plus interest ₹ 15/-.
(e) Our promissory note for ₹ 500/- in favour of A. Alam returned unpaid due to lack of instructions to the bank. A. Alam claim ₹ 510/- which we pay by cheque.
(J) Our promissory note for ₹ 500/- in favour of Patel settled by sending him Tanna’s acceptance of ₹ 500/-.
Solution:
Books of J. Jaggi:
Question 12.
X draws on Y a bill of exchange for ₹ 1500 on 1st April, 2005 for 3 months. Y accepts the bill and send it to X who gets it discounted for ₹ 1470. X immediately remits ₹ 490 to Y. On the due date, X, being unable to remit the amount due, accepts a bill for ₹ 2100 for three months which is discounted by Y for ₹ 2055. Y sends ₹ 370 to X. Before the maturity of the bill X becomes bankrupt his estate paying fifty paise in the rupee. Give the journal entries in the books of X and Y. Also show X’s account in Y’s books.
Solution:
(Bill discounted and Proceeds Shared. 2nd bill made to honour 1st bill):
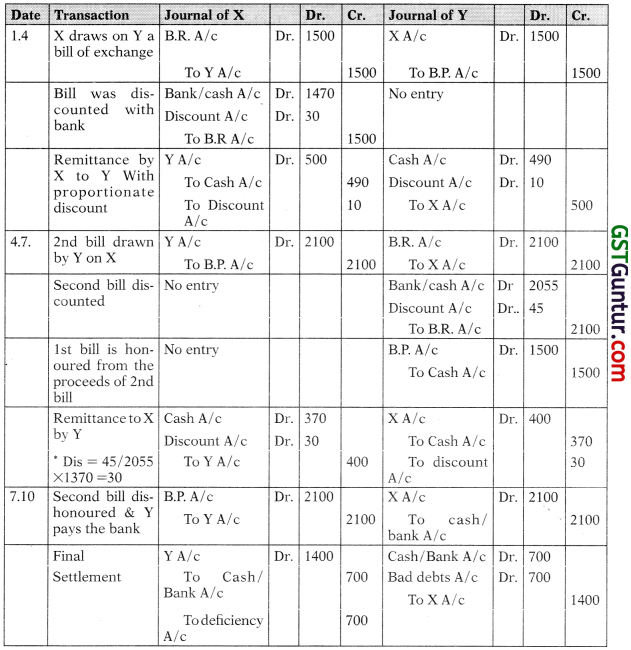
Out of the proceeds of 2nd bill ₹ 370 is used for X (₹ 1000 for honouring 1st bill which ‘X’ could not contribute & further ₹370 remitted to him) hence proportionate discount debited to him.
![]()
Question 13.
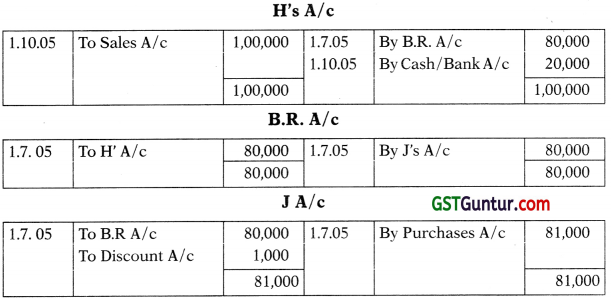
On 1st July, 2005 G drew a bill for ₹ 80,000 for 3 months on H for mutual accommodation. He accepted the bill of exchange. G had purchased goods worth ₹ 81,000 from J on the same date. G endorsed H’s acceptance to J in full settlement. On 1st September, 2005 J purchased goods worth ₹ 90,000 from H, J endorsed the bill of exchange received from G to H and paid ₹ 9,000 in full settlement of the amount due to H. On 1st October, 2005 H purchased goods worth X 1,00,000 from G. He paid the amount due to G by cheque. Give the necessary Journal Entries in the books of H and prepare necessary accounts in the books of H, G & J.
Solution:
Journal Entries:
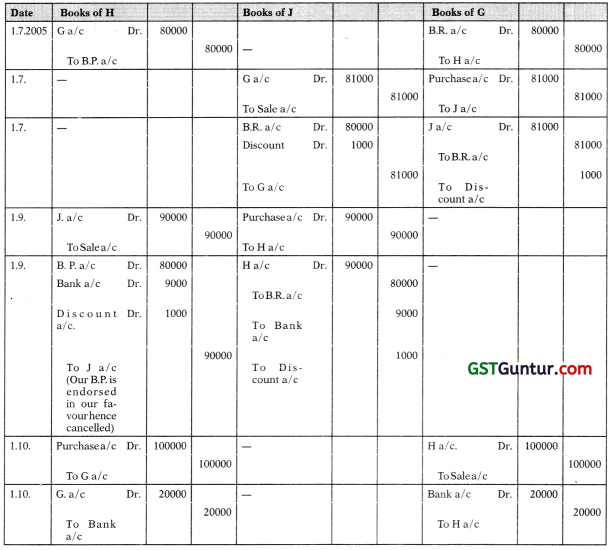
In The Books of ‘H’:
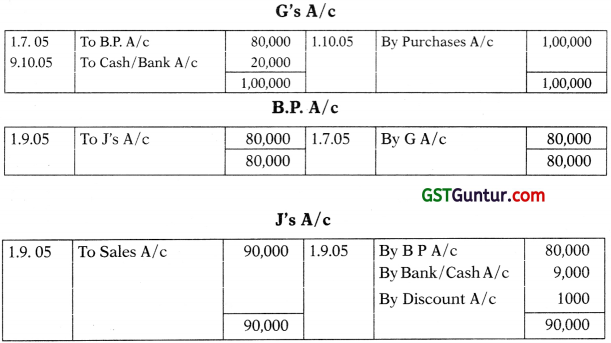
In The Books of ‘J’:
G’s A/c
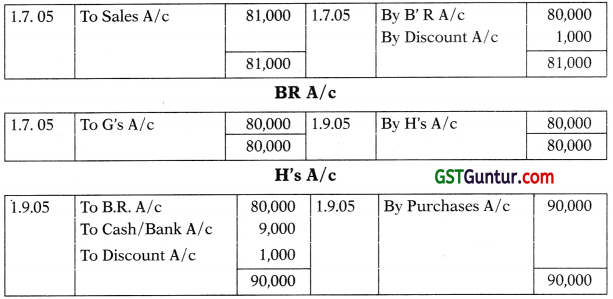
In The Books of ‘G’:
Question 14.
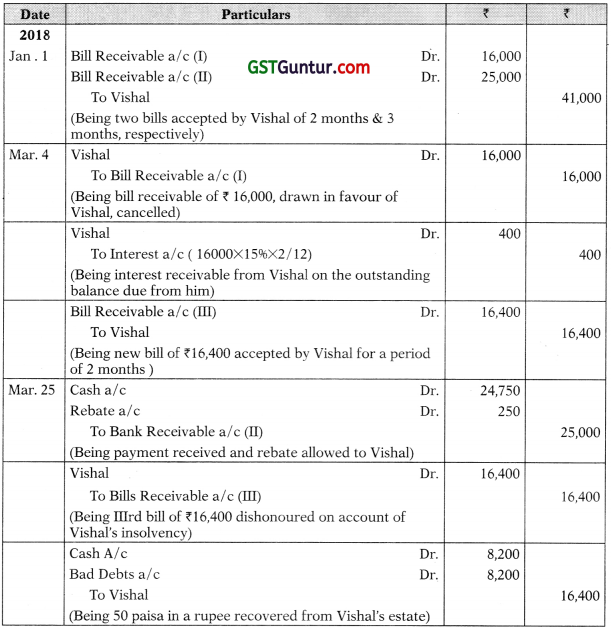
On 1st January 2018, Akshay draws two bills of exchange for ₹ 16,000 and Rs. 25,000. The bill of exchange for ₹ 16,000 is for two months while the bill of exchange for ₹ 25,000 is for three months. These bills are accepted by Vishal. On 4th March, 2018, Vishal requests Akshay to renew the first bill with interest @ 1596 p.a. for a period of two months. Akshav agreed to this proposal. On 25th March, 2018, Vishal retires the acceptance for Rs. 25,000, the interest rebate i.e. discount being ₹ 250. Before the due date of the renewed bill, Vishal becomes insolvent and only 50 paisa in a rupee could be recovered from his estate.
Show the Journal Entries (with narrations) in the books of Akshay.
Solution:
In the Books of Akshay:
True or False
Question 1.
Salary paid to Ram will be debited to Ram’s Personal account.
Answer:
False: Because salary paid to Ram will be debited to Salaries account as an expense of the business.
Question 2.
A promissory note can be made payable to the bearer.
Answer:
False: A promissory note cannot be made payable to the bearer. It is payable to or to the order of a certain person.
Question 3.
No cancellation entry is required when a bill is renewed.
Answer:
False: When the bill is renewed, entries are passed for cancellation of the old bill and for recording of the new bill.
Question 4.
At the time of Renewal of a bill, Interest account is debited in the books of a drawee.
Answer:
True: At the time of Renewal of a bill, interest account is debited in the books of a drawee as it represents an expense for him.
Question 5.
A bill given to a creditor is called bills payable.
Answer:
True: A bill given to a creditor is called Bills Payable.
![]()
Question 6.
A has drawn a bill on B. B accepts the same and endorses the bill to C.
Answer:
False: B cannot endorse the bill to C because he is a drawee. Only A, the drawer can do it.
Question 7.
Refusal by the acceptor to make payment of the bill on the maturity date is called Retirement of the bill.
Answer:
False: Refusal by the acceptor to make payment of the bill on the maturity date is called dishonour of the bill. Early payment of the bill is known as the Retirement of the bill.
Question 8.
Promissory Note requires acceptance
Answer:
False: Promissory note does not require acceptance, only bills receivable require acceptance.
Question 9.
Cancelling old bill and drawing new bill is called renewal of bill.
Answer:
True: When the acceptor of a bill fails to pay on the due date, a new bill may be drawn on him after cancellation of the old bill. This is known as renewal of a bill.
Question 10.
Discount at the time of retirement of a bill is a gain for the drawee.
Answer:
True: Discount at the time of retirement of a bill is a gain for the drawee.
