Section 194J TDS on Fees for Professional or Technical Services | Check Limit Here
Section 194J TDS Professional Technical Fees: The deduction of tax at source, or TDS, has proven to be quite effective in collecting taxes in the country by focusing on the source of income. It also makes paying tax easier for taxpayers when it comes time to file their income tax returns. This is due to the fact that they receive credit for taxes deducted at the source. In this article, let’s learn everything about Section 194J of the Income Tax Act 2020-21.
- What is Section 194J?
- Types of Payments Covered under Section 194J
- Rate of TDS under Section 194J
- Threshold Limit for Deducting Tax Under Section 194J
- Who is Liable to Deduct Tax Under Section 194J?
- Rate of Deduction of Tax Under Section 194J
- Time of Deduction Under Section 194J
- Time Limit for Payment of Tax Under Section 194J
- Consequences of Non-Deduction or Late Deduction under Section 194J
- FAQ’s on TDS on Professional or Technical Fees
What is Section 194J?
When certain payments are made to a specific resident, a person must deduct their Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) solely at the rate of 10%, according to the norms and regulations of Section 194J of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Types of Payments Covered under Section 194J
The following are the types of payments to residents mentioned under this section:
Professional Cases
Professional fees or fees for technical services are one of the most important and common types of payments that a corporate entity makes. Fees paid to a lawyer, doctor, engineer, architect, chartered accountant, interior decorators, advertisements, and others are examples of professional fees.
- It refers to the services provided by someone who works in the medical, architectural, legal, medical, or engineering fields. Accountancy, interior design, advertising, technical consulting, and any other profession recognised by the Board under Section 44AA are examples of additional services.
- Film artists, business secretaries, and approved representatives are among the other services permitted under Section 44AA.
- It also includes athletes, event managers, commentators, anchors, umpires and referees, coaches and trainers, physiotherapists, team physicians, and sports columnists.
Section 194J TDS on Fee for Technical Services
It refers to the consulting, technical, or managerial services provided by an individual. Assemblies, mining, and building are not considered technical services because the income earned falls under the recipient’s head salary.
Non-Compete Fees
For the purposes of Section 194J, non-compete fees refer to the amount paid in cash or in-kind in exchange for an agreement prohibiting the person from sharing any patent, licence, franchise, trademark, know-how, commercial or business rights, technique, or information that could be used elsewhere for manufacturing, processing, or any other provisional service.
Royalty
For the purposes of this section, royalty refers to payment in exchange for:
- Transfer of ownership of a patent, an innovation, a secret formula, a model, a design, or a trademark.
- Making use of an invention, a model, a patent, and so on.
- Sharing any information pertaining to the usage of an invention, patent, formula, or another such item.
- Equipment is used or has the right to be used for industrial, scientific, or commercial reasons.
- Transfer of rights to literary works, scientific results, films, or video recordings for radio broadcasting, with no regard for their sale, display, or distribution.
Specific Cases
TDS deduction is also available under Section 194J in the following instances, as determined by the department’s case laws and circulars:
- In hospitals, medical services are available.
- Film artists charge advertising companies professional fees.
- Amount paid to staff agencies and HR consultants.
- The payments are made by organizations to share registrants.
Rate of TDS under Section 194J
The rate of TDS under Section 194J is tabulated below:
| Payment Type | Threshold limit | Rate of tax |
| Fees for professional services | Rs. 30,000 | 10% |
| Fees for technical services and payment to call centres | Rs. 30,000 | 2% |
| Remuneration or fees to Director (other than 192) | NIL | 10% |
| Royalty | Rs. 30,000 | 10% |
| Non-compete fees | Rs. 30,000 | 10% |
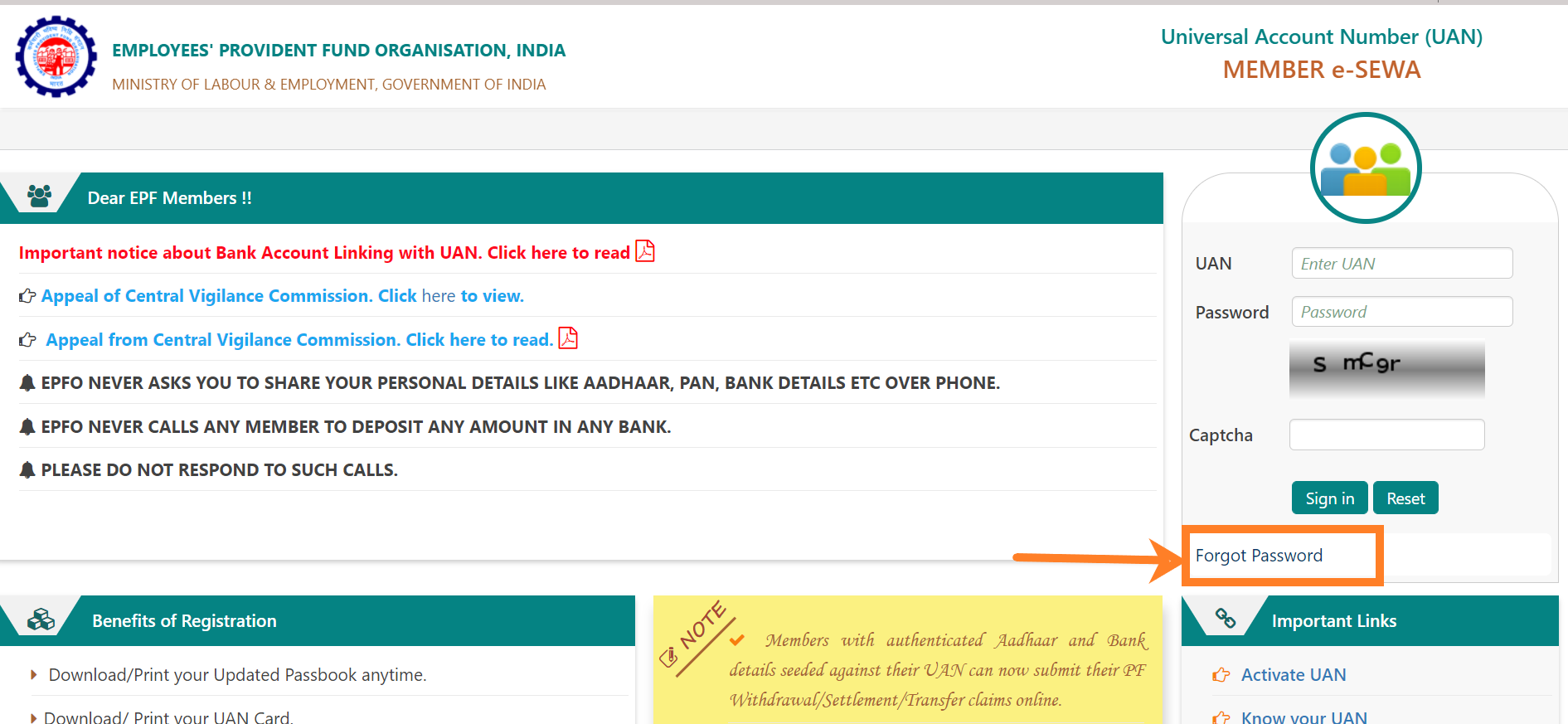
Threshold Limit for Deducting Tax Under Section 194J
If the payment is more than Rs. 30,000 during the year, the tax must be deducted. However, there is no limit for payments made to the director. No matter how small the amount, the tax must be deducted.
Who is Liable to Deduct Tax Under Section 194J?
With the following exceptions, everyone who makes a payment in the type of fees for professional or technical services is required to deduct tax at source:
- In the event of a sole proprietor or a HUF, when the preceding financial year’s turnover was less than Rs. 1 crore.
- In the event of an individual or a HUF operating on a business: If the preceding financial year’s turnover was less than Rs. 50 lakh.
- To put it another way, all entities (excluding people and HUF who were not subject to a tax audit the previous year) must deduct tax.
Rate of Deduction of Tax Under Section 194J
- TDS will be deducted at a rate of 10% on any payment made under this section.
- The payment of fees for technical services will be subject to TDS at a rate of 2% from April 1, 2020.
- With effect from April 1, 2017, the tax on payments made to call centre operators will be deducted at a reduced rate of 2%.
- In the event that the payee fails to provide his PAN, a 20% deduction will be made.
Time of Deduction Under Section 194J
The tax should be deducted if making the actual payment of the expense or making such an entry in the account whichever comes first.
Time Limit for Payment of Tax Under Section 194J
The time limit for submitting TDS under the section must be followed as follows:
- The deposit must be made on the same day as the TDS deduction under Section 194J is made by the government or on behalf of the government.
- TDS can also be deposited within a week after the end of the month in which the tax deduction was made.
- If the payment is made on the last day of the fiscal year, the TDS deposit must be made within two months of the end of the fiscal year in which the payment was made.
- If the assessing officer approves, some unusual instances may be allowed to deduct TDS on a quarterly basis.
| Non–Government deductor | Government deductor | |
| Payment made before 1st March | 7th day from the end of the month | 7th day from the end of the month |
| Payment made in the month of March | April 30th | Tax is paid on the date of payment to the payee, but the challan must be deposited by the 7th day following the month’s end. |
Consequences of Non-Deduction or Late Deduction under Section 194J
Disallowance of a portion of the expenditure: In the year in which the expenditure is claimed (added to the profit and loss account), 30% of the expenditure is disallowed; however, the 30% disallowed is re-allowed in the year in which the TDS is paid to the government.Interest charges till the date of payment: If the tax is not paid on time, interest must be paid to the government together with the TDS. The following formula is used to calculate the interest rate:
- Where no tax deduction has been made, interest at 1% per month/part of the month shall be levied from the date on which such tax was required to be deducted until the date of actual deduction.
- Where tax has been deducted but not paid to the government, From the date on which such tax was deducted until the date of payment to the government, interest at 1.5% per month/part of a month shall be charged.
FAQ’s on TDS on Professional or Technical Fees
Question 1.
Which section of the Income Tax Act enlists TDS on technical fees?
Answer:
Section 194J of the Income Tax Act enlists TDS on technical fees.
Question 2.
How is TDS on professional fees calculated?
Answer:
TDS on professional fees will be deducted at a rate of 10% under this section. TDS will be deducted at a rate of 20% if the income recipient does not provide his PAN to the deductor. There will be no surcharge, education cess, or SHEC added to the above-mentioned rates.
Question 3.
What is the maximum limit under Section 194J on TDS?
Answer:
The maximum limit under Section 194J is Rs.30,000, which applies to each item or payment separately.