Go through this Accounting Process-I – CS Foundation Fundamentals of Accounting and Auditing Notes will help students in revising the entire subject quickly.
Accounting Process-I – CS Foundation Fundamentals of Accounting Notes
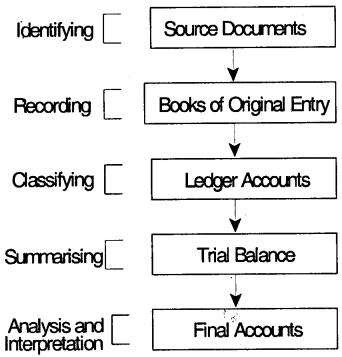
Accounting is the language of business – Accounting cycle/Accounting process:
Recording – Journal:
- A journal is a book of original entry/prime entry wherein transactions are first recorded before being posted to the ledger.
- A journal is that book of accounts in which transactions are original recorded in a chronological order.
- An entry done in a journal is called a journal entry and the process of recording a transaction In a journal is known as joumalising.
- A journal records both debit and credit aspects of a transaction.
A journal contains the following columns:
- Date : The date on which the transaction took place.
- Particulars : The two aspects (debit and credit) are recorded here.
- Ledger Folio (L.F.) : It records the page number in the ledger in which the accounts of the given entry are posted.
- Amount (Debit) : Debit amount is recorded in the Dr. column.
- Amount (Credit) : Credit amount is recorded in the Cr. column.
Specimen of Journal:
In the Books of ………
Journal Entries
| Date | Particulars | L.F | Debit Amount (₹) |
Credit Amount (₹) |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (v) |
Process of Journalising:
- Step – 1 : Ascertain what accounts are affected in the transaction.
- Step – 2 : Ascertain the nature of the account (i.e. real, nominal, personal etc.).
- Step – 3 : Apply the rules of debit and credit to each type of account.
- Step – 4 : Pass the entry.
Example:
Transaction – Rent paid in cash.
Step – 1 : Ascertain what accounts are affected.
Accounts affected are -Rent A/c and Cash A/c
Step – 2 : Ascertain the nature of account
Rent A/c – Nominal A/c (Expense)
Cash A/c – Real A/c (Asset)
Step – 3 : Apply golden rules of accounting:
Rent (Nominal A/c’s) – Debit all expenses
Cash A/c (Real) – Credit what goes out (as cash is going out of business)
Step – 4 : Pass the entry
Rent A/c Dr. (with the amount of rent)
To Cash A/c (Being rent paid in cash)
Note:
- The account to be credited is written proceeded by a word “To”.
- After every entry, a brief, description of the transaction is given in the next line of the entry. This is called narration and is written in brackets.
Points to Note:
- When goods are purchased “Purchase A/c” is debited, when goods are sold “Sales A/c” is credited.
- If it is not stated that purchase/sale is on cash/credit, it is assumed to be on credit.
- In a journal, the amount of debit and credit columns of each page are totaled and carried forward to the next page. Total c/f (carried forward)
- Sometimes a journal entry may have more than one debit or credit aspects. These types of entries are known as compound entries. The total of debit should be equal to total of credits or vice versa.
Example:
Mohan purchased goods worth ₹ 15,000. He got ₹ 1,000 as discount and paid ₹ 14,000 in cash.
Purchase A/c Dr. 15,000
To Cash A/c 14,000
To Discount received A/c 1,000
(Being goods purchased on discount)
Discount received is an income and is a Nominal A/c.
Ledger (Principal Book of Accounts):
- A ledger may be defined as a “book or register which contains in a summarized and classified form, a permanent record of all transactions”.
- It is a book which contains all set of accounts – (real, personal, nominal).
- Ledger is known as a principal book of account as it helps in the preparation of Trial Balance and financial statements (like P/L, B/S etc.)
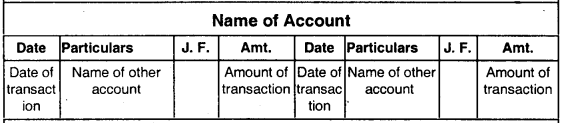
Format of ledger
(i) It has two sides left side is the debit side whereas right side is the credit side.
(ii) It has the following columns :
- Date – Date of transaction
- Particulars – Name of other account
- Journal folio (J. F.) – Page number of journal where entry was first recorded
- Amount: Amount of transaction
- Same columns will be there on the other side also.
Ledger posting:
(i) The process of transferring the information contained in a journal to a ledger is called posting.
(ii) Steps for posting:
For account debited in a journal entry:
- Step – 1 : Identify the ledger account to be debited
- Step – 2 : In the debit side of that A/c, post the other aspect of the entry in the particular column by writing the word “To ”.
- Step – 3 : Enter other details like amount J. F. and date.
(iii) Rules for posting:
- The name of the account in the journal and ledger should exactly be the same.
- The account debited in journal will be debited in ledger and the account credited in ledger will be credited.
- The word “To” will be added in the name of the accounts on the debit side and “By” will be added in the accounts on the credit side example : “To Sales”, “By Purchases” etc.
- The page number of the journal from where the entry is transferred is to be written in the Folio Column.
- The date of transactions is to be written in the date column.
Example
Rent paid in cash ₹ 10,000
Entry : Rent A/c Dr. 10,000
To Cash A/c 10,000
Posting Debit aspect of the entry – Rent A/c
Ledger Rent A/c
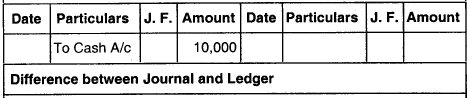
Difference between Journal and Ledger:
- Journal is book of original entry while ledger is book of second entry.
- Journal book is chronological while ledger is analytical.
- Process of recording in journal is “journalising” while the process of recording in ledger is known as “Posting”.
For an account credited in the journal entry:
- Step – 1 : Identify the ledger A/c to be credited
- Step – 2 : In the credit side of that account post the other aspect of the entry in the particular column by writing the word “By __________”.
- Step – 3 : Enter other details like date, amount J. F. (if any)
Example:
Taking same example as above
Rent A/c Dr. 10,000
To Cash A/c 10,000
Posting credit aspect of the entry:
Ledger Cash A/c
![]()
Balancing Ledger Account:
- After all entries are posted, both the sides of an account are totalled.
- For closing an account, both the side’s total shall be equal.
- If any side falls short of another, in order to make them equal, a balance figure is placed on the side which is short. This process is known as balancing of an account.
- If debit side total is more – the difference will be placed on credit side and it will be called as a debit balance.
- If credit side is more – the difference will be placed on the debit side and it will be called as a credit balance.
Note : The balance of an account is always known by the side which is greater.
Example : Lets take the Rent A/c of the above example
Rent A/c
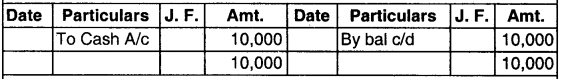
Debit side was more by ₹ 10,000 so balance has been written on the credit side to make them equal. This is a debit balance since debit side is more.
(v) Note that all ledger accounts (except Nominal Accounts) are balanced. The nominal accounts are transferred to P/L A/c.
Difference between Journal and Ledger:
| Basis | Journal | Ledger |
| Nature of Book | It is a book of primary entry. | It is a book of final entry. |
| Basis for Preparation | Primary documents (such as vouchers, receipts etc.) are the basis for recording transactions in the journal. | Journal is the basis for recording transactions in the ledger. |
| Stage of Recording | Recording in the Journal is the first stage. | Recording in the ledger is the second stage. |
| Process | The process of recording in Journal is called journalising. | The process of recording in the ledger is called posting. |
Subsidiary Book:
- Subsidiary books are the journals in which transactions of similar nature are recorded at the first instance.
- Recording all the entries in the journal will make the journal too lengthy and complicated. So for similar nature transactions separate journals are prepared which are known as subsidiary books.
- The transactions will first time be recorded in subsidiary books.
Types of subsidiary books:
1. Purchase Book – It records the credit purchase of goods traded in.
Ex- Stationery dealer purchased stationery in credit from Ram.
- Entries in the Purchase Book are made from the Invoice received from supplier at the end of week/month, total of Purchase Book is Debited to Purchases A/c in ledger.
- Entries in the purchase books are made from the invoice received from the supplier.
2. Sales Day Book:
- It records the credit sale of goods dealt in (traded in) Ex- Furniture dealer sold furniture on credit.
- Sales Book is prepared on the basis of copies of invoice sent to customers.
3. Purchase Return Book (Return Outward Book):
It records the goods or material returned to the supplier that have been purchased on credit. When goods are returned to the supplier a debit note is issued to him indicating that his account has been debited with the amount mentioned in the debit note.
4. Sales Return Day Book (Return Inwards Book):
It records the goods or material returned by the purchaser that had been sold on credit. When goods are returned by a customer a credit note is sent to him mentioning that his account has been credited with the value of goods returned.
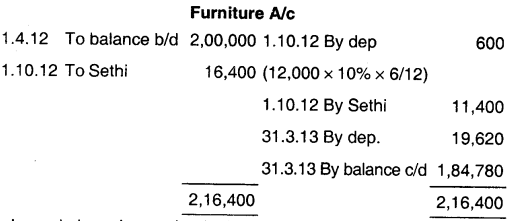
5. Bills Receivable Book:
It records the bills of exchange or promissory note received by a business entity.
6. Bills Payable Book:
It records the acceptance given to the creditor in the form of bills or promissory notes.
7. Cash Book:
It is used to record all cash transactions of the business.
8. General Journal OR Journal Proper:
All entries which cannot be recorded in the above subsidiary books are recorded in this book.
Example: opening entries, closing entries, rectification entries, purchase and sale of asset etc.
In Journal proper book, following types of transactions are recorded:
- opening journal entry
- closing journal entry
- adjustment entry
- transfer entry
- rectification entry
- purchase of fixed asset/stationary on credit
- sale of worn out or obsolete assets on credit
Cash Book:
- Cash book is a book of prime entry in which cash and bank transactions of a business are recorded in a chronological order.
- Cash book acts as both a book of original entry and a ledger. Hence, it is both a principal book and a subsidiary book. It records transaction concerning cash receipts and cash payments.
A cash book has two sides:
- Debit: Cash and cheques received are recorded here.
- Credit: Cash and cheque payments are recorded here.
Types of Cash Book:
It records only one aspect of transaction i.e. cash.
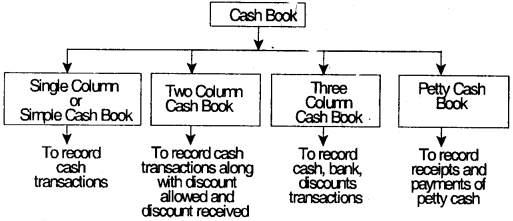
Single column or Simple cash book:
It is known as single column cash book because it contains only one amount column of cash.
Format of simple cash book:
Cash Book (Single Column)
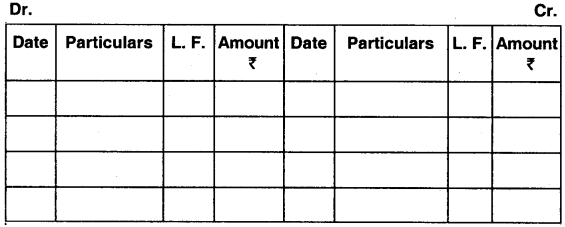
Double (two) column cash book
- It is so called because it has two amount columns on both sides cash column and discount column.
- Discount column on the debit side represents discount allowed while discount column on the credit side represents discount received.
Format of two column cash book
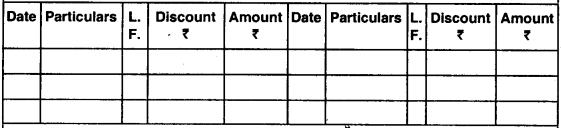
Three column (triple column) cash book:
- It is so called because it contains three amount columns
- Discount column, Cash column, Bank column
- Discount column – for discount received and allowed Cash column – cash received and paid
- Bank column – money deposited and money withdrawn from bank
- When triple column cash book is prepared there is no need for preparing a bank account in ledger.
Format of triple column cash book:
Cash Book (Triple Column)
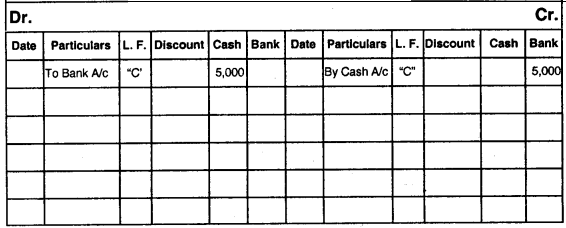
Concept of Contra Entry
- An entry which involves both cash and bank transactions is called a contra entry.
- These entries are posted on both sides of a cash book one in bank column and other in cash column, [on opposite sides]
- A letter “C” is written in L. F. column showing that the entry is a contra entry.
Example
Cash withdrawn from bank ₹ 5,000 Entry will be –
Cash A/c Dr. 5,000
To Bank A/c 5,000
(Being cash withdrawn from bank)
Showing the above entry in three column cash book
Cash Book (Triple Column)
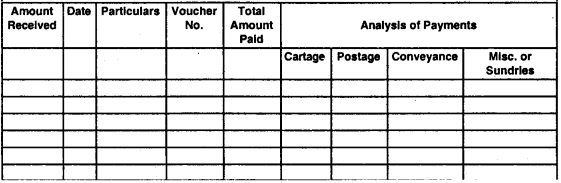
Petty Cash Book:
- Petty means small. A book which is used to record petty cash expenses of the business is called a petty cash book
- Petty cash book is maintained by a petty cashier
- The system by which petty cash book is maintained is known as “Imprest System”
- Petty cash book is treated either as a part of double entry system or as a Memorandum Book.
Note:
Imprest System:
Under this system, a fixed sum of money is given to the petty cashier for meeting expenses for a prescribed period called as Float. At the end of the period, if all the amount is used for meeting expenses, then the same fixed sum will be given to the petty cashier for the next period. If any balance is left, then the remaining amount will be given to the cashier for the next period.
Example:
If ₹ 500 are given to the cashier every month. For the month of January, he spends only ₹ 300 and 1200 are left with him. So, for the month of Feb, he will be given only additional ₹ 300 to complete ₹ 500.
The balance of petty cash book at the year end is shown as an asset.
Petty cash book has columns showing the amount allocated to various expenses.
Format petty cash book
Petty Cash Book
Trial Balance:
- “A trial balance is a statement prepared with the debit and credit balances of the ledger accounts including cash and bank balances to test the arithmetical accuracy of books”.
- Trial balance is a statement and not an account and it is not a part of double entry system.
- As per double entry system, totals of debit shall always be equal to totals of credit. To check this trial balance is prepared.
- All the accounts showing either a debit balance or a credit balance are placed in the trial balance and the debit and credit balances of the accounts are placed at the debit and credit columns respectively. At last, total of debit and credit columns are done.
- If both sides are equal – the accounts are arithmetically correct.
However, there may be some hidden errors.
Objectives of Trial Balance:
- Check arithmetical accuracy of ledger accounts.
- Helps in preparation of final accounts.
- Helps in detection of errors.
Methods of Preparing Trial Balance:
(i) Totals method:
Here totals of debits and credit columns of ledger accounts are taken to the trial balance.
(ii) Balance method:
Here the debit or credit balances of the ledger accounts are taken to the debit or credit column of trial balance respectively.
Format of Trial Balance
Specimen of Trial Balance
Trial Balance as at _______
Accounting Process-I MCQ Questions
1. The process of recording a transaction in the journal is called :
(a) Posting
(b) Journalising
(c) Tallying
(d) Casting
Answer:
(b) Journalising
2. Personal accounts are related to:
(a) Assets and liabilities
(b) Expenses, losses and incomes
(c) Debtors, creditors etc.
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(c) Debtors, creditors etc.
3. Goods given away as charity would be credited to :
(a) Sales A/c
(b) Purchase A/c
(c) Charity A/c
(d) Cash A/c.
Answer:
(b) Purchase A/c
4. Which of the following statements is true :
(a) Building account is a nominal account
(b) Outstanding rent account is a non-personal account
(c) Every debit has a corresponding credit
(d) Incomes are debited.
Answer:
(c) Every debit has a corresponding credit
5. Which one of the following is a personal account?
(a) Capital A/c
(b) Livestock Account
(c) Goodwill Account
(d) Outstanding salaries A/c.
Answer:
(d) Outstanding salaries A/c.
6. Payment of salary is recorded by:
(a) Debiting salary A/c crediting cash A/c
(b) Debiting cash A/c crediting salary A/c
(c) Debiting employee A/c crediting cash A/c
(d) Debiting employee A/c crediting salary A/c.
Answer:
(a) Debiting salary A/c crediting cash A/c
7. Debit means:
(a) An increase in asset
(b) An increase in liability
(c) A decrease in asset
(d) An increase in proprietor’s equity.
Answer:
(a) An increase in asset
8. Journal is a book of:
(a) Original entry
(b) Secondary entry
(c) All cash transactions
(d) All non-cash transactions.
Answer:
(a) Original entry
9. Which of the following is a cash transaction?
(a) Sold goods
(b) Sold goods to a customer
(c) Sold goods to a customer on credit
(d) Sold goods to a customer on account.
Answer:
(a) Sold goods
10. Received first and final payment of 60 paise in a rupee from the official receiver of: Mr. Ram who owed ₹ 2,000.
(a) Discount allowed A/c be debited with ₹ 800
(b) Bad debts recovered A/c be debited with ₹ 1,200
(c) Bad debt A/c be credited with ₹ 800
(d) Bad debt A/c be debited with ₹ 800.
Answer:
(d) Bad debt A/c be debited with ₹ 800.
11. Patent Right is :
(a) Personal Account
(b) Real Account
(c) Nominal Account
(d) Expense Account.
Answer:
(b) Real Account
12. The debts written of as bad, if recovered subsequently are :
(a) Credited to Bad Debts Recovered Account
(b) Credited to Debtors Account
(c) Debited to Profit and Loss Account
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Credited to Bad Debts Recovered Account
13. Insurance unexpired account is a:
(a) Real Account
(b) Personal Account
(c) Nominal Account
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Personal Account
14. A withdrawal of cash from business by the proprietor should be debited to:
(a) Drawing Account
(b) Capital Account
(c) Cash Account
(d) Purchase Account.
Answer:
(a) Drawing Account
15. If the total of debit side of an account exceeds the total of its credit side it indicates:
(a) Debit balance
(b) Credit balance
(c) Either debit or credit
(d) Neither debit nor credit.
Answer:
(a) Debit balance
16. Credit balance of a personal account indicates :
(a) Cash balance
(b) Amount payable
(c) Amount receivable
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Amount payable
17. Cash account will show :
(a) Debit or credit balance
(b) A credit balance
(c) A debit balance
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) A debit balance
18. The words To Balance bIV or ‘By Balance b/f are recorded in the ‘Particulars Column’ of an account at the time of positing of _______.
(a) An opening entry
(b) A closing entry
(c) An adjusting entry
(d) A transfer entry.
Answer:
(b) A closing entry
19. Normally, the following accounts are balanced :
(a) Personal accounts and nominal accounts
(b) Real accounts and nominal accounts
(c) Personal accounts and real accounts
(d) All accounts.
Answer:
(c) Personal accounts and real accounts
20. Ledger Book is popularly known as:
(a) Secondary book of accounts
(b) Principal book of accounts
(c) Subsidiary book of accounts
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(b) Principal book of accounts
21. Posting refers to the process of transferring information from _______.
(a) Journal to general ledger
(b) General ledger accounts to journals
(c) Source documents to journals
(d) Journals to source documents.
Answer:
(a) Journal to general ledger
22. L. F. (i.e., ledger folio column) in the journal is filled at the time of:
(a) Journalising
(b) Balancing
(c) Posting
(d) Casting.
Answer:
(c) Posting
23. The cash book records :
(a) All Cash Receipts
(b) All Cash Payments
(c) All Cash Receipts and Payments
(d) Cash and Credit Sale of Goods.
Answer:
(c) All Cash Receipts and Payments
24. Cash book is a:
(a) Subsidiary Book
(b) Subsidiary Journal and Ledger
(c) Ledger Account
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Subsidiary Journal and Ledger
25. Which of the following will be recorded as contra entry :
(a) Withdrew from bank for personal use
(b) A cheque received from X lodged into bank on the same day
(c) A cheque received from Y a week earlier lodged into bank
(d) A customer directly deposited the money in our bank account.
Answer:
(c) A cheque received from Y a week earlier lodged into bank
26. Cash book does not record :
(a) Credit Purchases
(b) Credit sales
(c) Outstanding expenses
(d) All the above transactions.
Answer:
(d) All the above transactions.
27. The balance in the petty cash book is:
(a) An expenses
(b) A profit
(c) An asset
(d) A liability.
Answer:
(c) An asset
28. Balance of cash book is posted to the ledger _______.
(a) In the cash account
(b) In bank account
(c) Nowhere
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer:
(c) Nowhere
29. A cheque received and deposited in the same day is recorded in the:
(a) Cash column of the cash book
(b) Bank column of the cash book
(c) Credited in the cash book
(d) Debited in the cash book
Answer:
(b) Bank column of the cash book
30. Which is entered on the debit side of cash book?
(a) Trade discount allowed
(b) Trade discount received
(c) Cash discount allowed
(d) Cash discount received.
Answer:
(c) Cash discount allowed
31. In a three column Cash Book :
(a) Only cash column and discount columns are balanced
(b) Only bank column and discount columns are balanced
(c) Only cash column and bank columns are balanced
(d) Cash column, bank column and discount columns are balanced.
Answer:
(c) Only cash column and bank columns are balanced
32. Purchases book is used to record :
(a) All purchases of goods
(b) All credit purchases
(c) All credit purchase of goods
(d) All credit purchases of assets other than goods.
Answer:
(c) All credit purchase of goods
33. Sales returns book is used to record :
(a) Returns of fixed assets sold on credit
(b) Returns of goods sold for cash
(c) Returns of goods sold on credit
(d) Sales of goods.
Answer:
(c) Returns of goods sold on credit
34. Purchase for office furniture on account is recorded in:
(a) General journal
(b) Cash book
(c) Purchases book
(d) Sales book.
Answer:
(a) General journal
35. A periodic total of the purchase book is :
(a) Posted to the debit of the Purchase Account
(b) Posted to the debit of the Sales Account
(c) Posted to credit of the Purchases Account
(d) Posted to the credit of Sales A/c.
Answer:
(a) Posted to the debit of the Purchase Account
36. Acceptances received and recorded in Bills Receivable Book are transferred to ledger:
(a) On the debit side of relevant personal accounts
(b) On the credit side of relevant personal account
(c) Nowhere
(d) Either (a) or (b)
Answer:
(b) On the credit side of relevant personal account
37. Closing entries are recorded in :
(a) Cash Book
(b) Ledger
(c) Journal proper
(d) Balance sheet.
Answer:
(c) Journal proper
38. The following is entered in the journal proper:
(a) Trade discount allowed
(b) Trade discount received
(c) Cash discount allowed
(d) Opening entry.
Answer:
(d) Opening entry.
39. Credit purchase of stationery by a stationery dealer will be recorded in:
(a) Purchase Book
(b) Sales Book
(c) Cash Book
(d) Journal proper (General Journal)
Answer:
(a) Purchase Book
40. A debit note issued to a creditor for goods returned by us is to be recorded in the:
(a) Bills Receivable Bank
(b) Purchases Book
(c) Journal proper (General Journal)
(d) Purchases Return Book.
Answer:
(d) Purchases Return Book.
41. A Return Inwards Book is kept to record:
(a) Returns of goods sold
(b) Returns of anything purchased
(c) Returns of goods purchased
(d) Returns of anything sold.
Answer:
(a) Returns of goods sold
42. Journal proper is used to record:
(a) All cash purchases of assets other than goods
(b) All cash sales of assets other than goods
(c) Returns of fixed assets purchased on credit
(d) Recovery of an amount already written off as bad debts.
Answer:
(c) Returns of fixed assets purchased on credit
43. A second hand motor car was purchased on credit from Mohan will be recorded in the _______.
(a) Journal proper (General Journal)
(b) Sales Book
(c) Cash Book
(d) Purchase Book.
Answer:
(a) Journal proper (General Journal)
44. Which of these is a method of preparation of Trial Balance?
(a) Total method
(b) Balance method
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None.
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
45. If Trial Balance tallies, it surely means that there are no errors in books of account. This statement is _______.
(a) True
(b) False
(c) Partly True
(d) None.
Answer:
(b) False
46. In a journal, if it is not stated that purchase or sale is on credit or cash, it is assumed to be on _______.
(a) Cash
(b) Credit
(c) Any of the above
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Credit
47. Which of the following is both a principal as well as a subsidiary book?
(a) Sales Book
(b) Purchase Book
(c) Cash Book
(d) Bills Receivable Book
Answer:
(c) Cash Book
48. Goods worth ₹ 25,000 sold to Amit will be recorded in journal as:
(a) Debit the sales A/c & credit Amit A/c
(b) Credit sales A/c & debit Amit A/c
(c) Debit sales A/c & credit cash A/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Credit sales A/c & debit Amit A/c
49. Payment of electricity bill of the proprietor’s house will be debited to:
(a) Drawings A/c
(b) Cash A/c
(c) Electricity A/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Drawings A/c
50. If goods worth ₹ 10,000 are stolen, then it shall be recorded in:
(a) Purchase Book
(b) Journal Proper
(c) Purchase Return Book
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) Journal Proper
51. If the business issues a debit note to the seller of such goods, the entry will be passed in:
(a) Purchase book
(b) Purchase return book
(c) Sales book
(d) Sales return book
Answer:
(b) Purchase return book
52. The total of purchase book will be posted in ledger on:
(a) Debit side of purchase A/c
(b) Credit side of purchase A/c
(c) Credit side of cash A/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Debit side of purchase A/c
53. The total of sales book will be posted in ledger in:
(a) Debit side of sales A/c
(b) Credit side of sales A/c
(c) Debit side of cash A/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Credit side of sales A/c
54. The total of purchase return will be taken in the ledger in:
(a) Debit side of purchase return A/c
(b) Credit side of purchase return A/c
(c) Debit side of cash A/c
(d) Credit side of cash A/c
Answer:
(b) Credit side of purchase return A/c
55. The total of sales return will be recorded in the ledger by:
(a) Debiting sales return A/c
(b) Crediting sales return A/c
(c) Crediting cash A/c
(d) Debiting cash A/c
Answer:
(a) Debiting sales return A/c
56. Which of the following transactions will be recorded in the sales book of Bharat Furnitures & Co.?
(a) Sold Table for cash ₹ 10,000
(b) Sold Chair to Mehra & Co. for ₹ 12,000
(c) Sold an old Typewriter for ₹ 2,000 to Verma & Co.
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(b) Sold Chair to Mehra & Co. for ₹ 12,000
57. Which of the following transactions will be recorded in the purchase book of Sharma Cloth House?
(a) Purchased Cloth worth ₹ 2,000 for cash
(b) Purchased stationery worth ₹ 200 on credit
(c) Purchased cloth worth ₹ 5,000 from Verma Garments
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Purchased cloth worth ₹ 5,000 from Verma Garments
58. _______ is prepared to ensure arithmetical accuracy of the accounts.
(a) Ledger
(b) Balance Sheet
(c) Trail Balance
(d) P & L A/c
Answer:
(c) Trail Balance
59. Which of the following is NOT included in Trial Balance?
(a) Closing stock
(b) Opening stock
(c) Suspense A/c
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Closing stock
60. If the trial balance is NOT reconciled, then it is reconciled by opening:
(a) Suspense A/c
(b) Reconciliation A/c
(c) Miscellaneous A/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Suspense A/c
61. The trial balance is a:
(a) Account
(b) List
(c) Subsidiary book
(d) Statement
Answer:
(d) Statement
62. The overdraft balance in the Savings A/c of the bank will be at the _______.
(a) Debit side of Bank column
(b) Credit side of Bank column
(c) Neither (a) nor (b)
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(b) Credit side of Bank column
63. The closing balance of Wages A/c is transferred to:
(a) P & L A/c
(b) Trading A/c
(c) Balance sheet
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Trading A/c
64. Which of the following transactions are recorded in purchase book?
(a) All purchases made during the year
(b) Only credit purchases during the year
(c) Only credit purchases of goods traded by the firm
(d) None the above
Answer:
(c) Only credit purchases of goods traded by the firm
65. Goods destroyed by fire will be credited to:
(a) Fire A/c
(b) Purchases A/c
(c) P&LA/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Purchases A/c
66. If goods worth ₹ 500 are taken by the proprietor for personal use, the entry will be:
(a) Debit Drawings A/c, Credit Purchases A/c
(b) Debit Purchases A/c, Credit drawings A/c
(c) Debit Proprietor A/c, Credit Purchases A/c
(d) Credit Proprietor A/c, Debit stock A/c
Answer:
(a) Debit Drawings A/c, Credit Purchases A/c
67. The Balance in the bank pass book is:
(a) Debit
(b) Credit
(c) Both Debit & Credit
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Both Debit & Credit
68. If the owner of a business gives his personal car to the business, then which A/c will be debited and credited:
(a) Debit Capital A/c & Credit Car A/c
(b) Debit Car A/c & Credit Capital A/c
(c) Debit Car A/c & Credit Cash A/c
(d) Debit Car A/c & Credit Drawings A/c
Answer:
(b) Debit Car A/c & Credit Capital A/c
69. If the goods are destroyed by fire and the insurance company accepts the full claim, then the entry will be :
(a) Debit Insurance Co., Credit Cash
(b) Debit Insurance Co., Credit Purchase
(c) Debit Cash, Credit Purchase
(d) Debit Purchase, Credit Cash
Answer:
(b) Debit Insurance Co., Credit Purchase
70. If Ajay sells his car and brings the proceeds in the business, then the entry will be:
(a) Debit Car, Credit Cash
(b) Debit Car, Credit Capital
(c) Debit Cash, Credit Capital
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Debit Cash, Credit Capital
71. If goods worth ₹ 1,00,000 are sold at a trade discount of 10%, then the amount to be entered in discount is:
(a) 10,000 (Dr.)
(b) Zero
(c) 10,000 (Cr.)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Zero
72. Capital A/c is a:
(a) Real A/c
(b) Personal A/c
(c) Nominal A/c
(d) Both (a) & (c)
Answer:
(b) Personal A/c
73. Which A/c is credited in case of bad debts?
(a) Cash A/c
(b) Bad Debts
(c) Debtors A/c
(d) P&LA/c
Answer:
(c) Debtors A/c
74. Goods given on charity will be credited to:
(a) Charity A/c
(b) Goods A/c
(c) Purchases A/c
(d) Sales A/c
Answer:
(c) Purchases A/c
75. Prepaid Salary is a:
(a) Real A/c
(b) Nominal A/c
(c) Personal A/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Personal A/c
76. is sent to a supplier on returning the goods:
(a) Debit Note
(b) Invoice
(c) Credit Note
(d) Material Receipt
Answer:
(a) Debit Note
77. Trade discount:
(a) To recorded in the discount A/c
(b) Not recorded in the books at all
(c) Recorded only in case of
(d) Not to be considered in determining special cases the net sales price
Answer:
(b) Not recorded in the books at all
78. The expired portion of capital expenditure is shown in the financial statement is:
(a) An income
(b) An expense
(c) An asset
(d) A liability
Answer:
(b) An expense
The expired portion of capital expenditure is known as depreciation. Since, depreciation is treated as expenses, it is transferred to debit side of P/L A/c. So, expired portion of capital expenditure is shown in financial statement as an expenses.
79. Maintaining petty cash book is:
(a) Mandatory
(b) Necessary
(c) Dependant on nature of business
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(c) Dependant on nature of business
Payments in cash of small amount like travelling, postage, refreshment etc. are petty cash expenses. In big organisation, it is not possible to maintain petty expenses for main cashier. In small organisation the number of petty expenses is less.
So, maintaining petty cash book is dependent on nature of business.
80. Purchase book records:
(a) All purchases made by the firm
(b) All purchases of fixed asset used by the firm
(c) Credit purchases of goods dealt in by the firm
(d) Cash purchases of goods dealt in by the firm.
Answer:
(c) Credit purchases of goods dealt in by the firm
Purchase book is meant for recording the purchase of goods on credit only. Because cash purchase are recorded in the cash book.
81. Sales Book is prepared:
(a) On the basis of Cash Book
(b) On the basis of copies of invoices.
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) On the basis of sales orders.
Answer:
(b) On the basis of copies of invoices.
In the sales book, only credit sale of goods are recorded, sales book is prepared on the basis of copies of invoice sent to customers.
82. Expenses paid in cash and recorded as assets before they are used are called _______.
(a) Accrued Expenses
(b) Interim Expenses
(c) Prepaid Expenses
(d) Unearned Expenses
Answer:
(c) Prepaid Expenses
Expenses paid in cash and recorded as assets before they are used are called prepaid expenses. Those expenses which have been paid in advance and whose benefit will be available in future are called prepaid expenses.
Example : insurance premium, rent etc. paid in advance.
83. In which book does the cash sales will be recorded _______.
(a) Cash Book
(b) Purchase Book
(c) General Journal
(d) Sales Book.
Answer:
(a) Cash Book
In sales book, only credit sales are recorded. Cash sales will be recorded in cash book because all cash receipts are recorded in cash book on credit side.
84. Which of the following transactions would have no impact on owner’s capital?
(a) Purchase of land from the proceeds of a bank loan
(b) Withdrawal of profits
(c) Net loss
(d) Cash brought in by owner as additional capital
Answer:
(a) Purchase of land from the proceeds of a bank loan
Withdrawal of profit is a drawings and drawings is reduced from the owner’s capital. Net loss reduces the capital. Cash brought in by owner as additional capital increase the owner’s capital. Thus these three transaction would have impact on owner’s capital. On taking a bank loan, the following entry will be passed
Cash A/c Dr.
To Bank Loan A/c
On purchase of Land the following entry will be passed –
Land A/c Dr.
To Cash A/c
On considering these entry we found that purchase of land from the proceeds of a bank loan would have no impact on owner’s capital.
85. Which of the following accounts will be credited, when the goods are purchased for cash?
(a) Stock Account
(b) Cash Account
(c) Supplier’s Account
(d) Work in progress Account
Answer:
(b) Cash Account
When the goods are purchased for cash, the following entry will be passed –
Purchase A/c Dr.
To Cash A/c
So, cash A/c will be credited.
86. Which of the following would not be regarded as an asset?
(a) A piece of equipment owned by a business
(b) A sum of money owned by the business
(c) An inventory of goods that is yet to be sold
(d) A building that has been taken on rent by the business for its use.
Answer:
(d) A building that has been taken on rent by the business for its use.
A piece of equipment owned by a business is treated as fixed assets. A sum of money owned by the business is treated as current assets.
An inventory of goods that is yet to be sold is treated as closing stock which is an asset A building that has been taken on rent by the business for its use would not be regarded as an asset because company have no ownership of that building.
87. Withdrawal of cash from bank for official use will result into:
(a) Increase of assets
(b) Increase of expenses
(c) No impact on assets
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) No impact on assets
On withdrawal of Cash from bank for office use the following entry will be passed –
Cash A/c Dr.
To Bank A/c
This entry will have no impact on assets since, on one hand, cash A/c will increase and on the other hand, bank A/c will decrease.
88. Franchise rights, goodwill and patents are the examples of:
(a) Liquid Assets
(b) Tangible Assets
(c) Intangible Assets
(d) Current Assets
Answer:
(c) Intangible Assets
Franchise rights, goodwill and patents are the example of Intangible Assets. As intangible Assets are those assets which cannot be seen or touched or felt and there is no physical form to show it.
89. Which of the following is not an example of current asset?
(a) Prepaid Expenses
(b) Account Receivables
(c) Short term securities
(d) Unearned Income.
Answer:
(c) Short term securities
Current assets are those that are meant to be converted into cash as soon as possible.
Example : stock of goods, prepaid expenses, account receivable, unearned income.
Short term securities are regarded as Liquid Assets and not as current assets.
90. The three columns on each side of a three columnar cash book represent:
(a) Real and personal accounts
(b) Real and nominal accounts
(c) Personal and nominal accounts
(d) Real, personal and nominal accounts.
Answer:
(d) Real, personal and nominal accounts.
The three columns in a three columnar cash book represent Real Personal and Nominal Accounts
- Discount column : Nominal account
- Cash column : Real account
- Bank column : Personal account
91. A chronological record of transaction may be found in:
(a) Balance Sheet
(b) Trial Balance
(c) Ledger
(d) Journal.
Answer:
(d) Journal.
A chronological record of transaction may be found in “Journal” Journal records transactions on a day to day basis and as and when they occur.
92. A purchased an old computer costing ₹ 10,000 and incurred ₹ 1,000 on its repairs and ₹ 500 on its packing. He sold the computer at 20% margin on selling price. The sales value will be:
(a) ₹ 12,500
(b) 711,000
(c) 714,375
(d) 713,800.
Answer:
(c) 714,375
Total cost of computer:
10,000 + 1,000 + 500 = 11,500
Margin is 20% on selling price which means it is 25% on cost.
∴ Sales value will be 11,500 + 25%
= ₹ 14,375/-
93. The imprest system pertains to _______.
(a) Purchase book
(b) Sales book
(c) Cash book
(d) Petty cash book.
Answer:
(d) Petty cash book.
It is convenient to entrust a definite sum of money to the petty cashier in the beginning of a period and to reimburse him for payments made at the end of the period. Thus, he will have again the fixed amount in the beginning of the new period. Such a system is known as the imprest system of petty cash book.
94. The statement showing balance of all the ledger accounts is known as _______.
(a) Trial balance
(b) Balance sheet
(c) Bank reconciliation statement
(d) Profit and loss account.
Answer:
(a) Trial balance
Trial Balance is a statement which shows closing balances of all the ledger accounts.
95. A General Cash book acts as a _______.
(a) Journal
(b) Ledger
(c) Both
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Both
A cashbook is a book of prime entry in which cash and bank transactions of business are recorded. It acts as a book of original entry and a ledger. Hence, it is both Journal and Ledger.
96. Debit note is related with the _______.
(a) Sales book
(b) Sales return book
(c) Purchase return book
(d) Journal proper.
Answer:
(c) Purchase return book
When the goods or material are returned to the supplier that have been purchased on credit, a debit note is issued to him indicating that his account has been debited with the amount mentioned in the debit note. Thus, debit note is related with purchase return book.
97. If assets are increased by 2,000 and liabilities are increased by 1,200. What will be the effect on business equity?
(a) 800
(b) 2,000
(c) 3,200
(d) 1,200.
Answer:
(a) 800
Business Equity = Total assets – Total outside liabilities = 2,000 – 1,200 = 800
98. In case of Trial Balance, balance comes from ___________.
(a) Journal
(b) Ledger
(c) Balance Sheet
(d) Profit & Loss a/c.
Answer:
(b) Ledger
A trial balance is the list of balances of both credit and debit extracted from various accounts in the ledger including cash and bank balances.
99. Cost of goods sold – 60,000.
Sales- 95,000
Expenses – 20,000
Gross Profit will be?
(a) 20,000
(b) 15,000
(c) 35,000
(d) 1,75,000.
Answer:
(c) 35,000
Cost of Goods Sold = ₹ 60,000
Sales = ₹ 95,000
Gross Profit = Sales – Cost of Goods Sold
= 95,000 – 60,000
= 35,000
Hence, option (c) is correct.
100. Why ledger is made?
(a) To classify all items appearing in Journal
(b) To record the transaction
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) To classify all items appearing in Journal
Journalising means recording the transaction while posting means posting & classification of all the items of journal in respective accounts of ledger.
Hence, ledger is made to classify all items appearing in journal.
101. In case of three columnar cash book, contra entry _______.
(a) Bank account only
(b) Cash and discount account
(c) Cash account only
(d) Cash and bank account
Answer:
(d) Cash and bank account
Three columnar cash book contains the following three amounts columns on each side:
- Discount Column
- Cash Column
- Bank Column
In a case of Contra Entry i.e. a transaction involves both cash and bank accounts, it is entered on both sides of the cash book, one in the cash column and other in the bank column, though on opposite sides.
102. The closing entry for transfer of Salaries Paid A/c appearing in the Trial Balance will be:
(a) Debit Salaries A/c, Credit P&L A/c
(b) Debit Salaries A/c, Credit Trading A/c
(c) Debit Trading A/c, Credit Salaries A/c
(d) Debit P&L A/c, Credit Salaries A/c
Answer:
(d) The closing entry for transfer of salaries paid a/c appearing in trial balance will be.
Profit & Loss A/c Dr.
To Salaries A/c
103. Which of the following statement is incorrect with respect to a journal entry?
(a) It is prepared to record all transactions in alphabetical order
(b) It should always end with a narration explaining the need for it
(c) It should be substantiated by appropriate voucher and authority
(d) It should always consist of a debit entry matched by a corresponding credit entry.
Answer:
(a) It is prepared to record all transactions in alphabetical order
- Journal entry should always end with a narration explaining the purpose for it.
- It should be recorded on the basis of appropriate voucher and authority.
As a rule, every transaction have two sides i.e. debit and credit side. It is that book of account in which transactions are recorded in a chronological (day to day) order.
So, option (a) is incorrect about Journal entry i.e. to record all the transactions in alphabetical order.
104. Which of the following entries will be entered in the Journal proper?
(a) Sold goods on credit
(b) Goods purchased and paid by cash
(c) Furniture purchased on credit
(d) Purchase goods on credit.
Answer:
(c) Journal proper is used for making the original record of such transaction for which no special journal has been kept in the business. Some entries confined to general journal (or journal proper) are:
- Opening entries
- Closing entries
- Adjustment entries
- Rectification entries
- Purchase of fixed assets etc.
Therefore, furniture purchased on credit will be entered in journal proper.
105. Which of the following account will be credited for profit on sale of fixed assets?
(a) Depreciation Account
(b) Cash Account
(c) Fixed Asset Account
(d) Profit and Loss Account.
Answer:
(d) Profit and Loss Account.
When a fixed asset is sold at a profit then the account to be credited will profit and loss account. Suppose furniture of W.D.V ₹ 10,000 is sold for ₹ 12,000.
Cash/Bank A/c Dr. 12,000
To Furniture A/c 10,000
To P/L A/c 2,000
106. A chronological record of transactions may be found in _______.
(a) Trial balance
(b) Journal
(c) Balance sheet
(d) Ledger.
Answer:
(b) Journal
In Journal, which is primary book for recording transactions of business, transactions are recorded in chronological order.
107. The imprest system pertains to:
(a) Purchase book
(b) Cash book
(c) Sales book
(d) Petty Cash book.
Answer:
(d) Petty Cash book.
Imprest system of petty cash book, under this system the petty cashier is given a definite sum at beginning of a certain period. This amount is called imprest amount.
108. After the preparation of income statement, it was discovered that accrued expenses of ₹ 1,000 have been ignored and closing inventory has been overvalued by ₹ 1,300. This will have result in:
(a) An understatement of net profit of ₹ 2,300
(b) An overstatement of net profit of ₹ 300
(c) An understatement of net profit of ₹ 300
(d) An overstatement of net profit of ₹ 2,300.
Answer:
(d) An overstatement of net profit of ₹ 2,300.
If accrued expenses of ₹ 1,000 have been ignored, this will increase the net profit by ₹ 1,000.
If closing inventory is overvalued, it will also result in increasing the net profit by ₹ 1,300.
Thus, net effect will be profit increased by ₹ 2,300.
109. Where Rent prepaid comes in Balance Sheet?
(a) Asset side
(b) Liability side
(c) Does not come in Balance Sheet
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Asset side
Those expenses which have been paid in advance and whose benefit will be available in future are called prepaid expenses. These are shown as assets in the balance sheet.
110. If capital is ₹ 10,000, creditors ₹ 5,000, B/P ₹ 2,000. Machinery ₹ 2,000, Prepaid expenses ₹ 1,000. Land and Building ₹ 5,000. Find the value of Debtors is:
(a) ₹ 7,000
(b) ₹ 12,000
(c) ₹ 9,000
(d) ₹ 8,000
Answer:
(c) ₹ 9,000
Total liabilities = Capital + Creditors + Bills payable
= 10,000 + 5,000 + 2,000
= ₹ 17,000
Memorandum Balance Sheet:
| Liabilities | Amount | Assets | Amount |
| Capital | 10,000 | Machinery | 2,000 |
| Creditors | 5,000 | Prepaid Expense | 1,000 |
| Bills Payable | 2,000 | Land, Building | 5,000 |
| Debtors | 9,000 | ||
| Total | 17,000 | 17,000 |
As per matching concept Assets should be equal to Total Liabilities.
Total Assets = Machinery + Land + Prepaid expense
= 2,000 + 1,000 + 5,000
= ₹ 8,000
Thus, the difference of ₹ 9,000 is the amount of Debtors.
111. B/P ₹ 20,000, creditors ₹ 10,000, Debtors ₹ 5,000, Investment ₹ 2,00,000 Plant and Machinery is ₹ 1,50,000, closing stock is ₹ 20,000 find the capital:
(a) ₹ 3,55,000
(b) ₹ 2,00,000
(c) ₹ 3,44,000
(d) ₹ 3,45,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 3,45,000
Total Outside liabilities = Bills Payable + Creditors
= 20,000 + 10,000
= ₹ 30,000
Total Assets = Debtors + Investment + Plant & Machinery + Closing Stock
= 5,000 + 2,00,000 + 1,50,000 + 20,000
= ₹ 3,75,000
Capital = Total Assets – Outside liabilities = 3,75,000 – 30,000
= ₹ 3,45,000
112. What we give at the time of sales return:
(a) Credit Note
(b) Invoice
(c) Debit Note
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Credit Note
We give Credit note at the time of Sales return. The Individual accounts of the customers are credited with the respective amounts while the periodical total of Sales return book is posted to the debit of Sales return account.
113. A cheque received from a customer and deposited on the same day is recorded in the:
(a) Debit side of cash column in the cash book
(b) Credit side of cash column in the cash book
(c) Debit side of bank column in the cash book
(d) Credit side of bank column in the cash book.
Answer:
(c) Debit side of bank column in the cash book
A cheque received from a customer and deposited on the same day is recorded on the debit side of the bank column in the cash book as on the debit side, all cash receipts are recorded while on the credit side, all cash payment are recorded. Cash Book thus serves the purpose of a book of original entry as well as that of ledger account.
114. A building is purchased from office cash for use by the building. Which of these would represent the entry for the transaction?
(a) Debit an asset account, credit a sales account
(b) Debit building account, credit cash account
(c) Debit the bank account, credit on expense account
(d) Debit a liability account, credit on expense account.
Answer:
(b) Debit building account, credit cash account
A building purchased from office cash would end up with the entry for the transaction as:
Building Account Dr.
To Cash Account
115. The trial balance of a proprietary concern shows the following balances: Capital ₹ 2,00,000, Income Tax ₹ 12,000, Income Tax paid in advance ₹ 4,000 and Interest on advance payment of tax ₹ 200. What will be the balance of capital at end?
(a) ₹ 1,83,800
(b) ₹ 1,84,200
(c) ₹ 1,88,000
(d) ₹ 1,84,000
Answer:
(b) ₹ 1,84,200
| Capital | 2,00,000 |
| (+) Interest on Advance Tax | 200 |
| (-) Income Tax Paid | 12,000 |
| (-) Income Tax Paid in advance | 4,000 |
| Total | 1,84,200 |
116. A debit note for ₹ 2,000/- issued to Mr. F for goods returned. This will be accounted in:
(a) Journal proper (General Journal)
(b) Purchase return book
(c) Bills receivable book
(d) Purchase book.
Answer:
(b) Purchase return book
A debit note for ₹ 2,000 issued to Mr. F for goods returned. This will be accounted in purchase return book. This book records the details of goods returned by the business organisation to the supplier. When the goods are returned to the supplier, a debit note is sent to him indicating that his account has been debited with the amount mentioned in the debit note.
117. The closing entry for transferring purchase return appearing in trial balance will be:
(a) Debit purchase return account, Credit Profit and Loss Account
(b) Debit trading account, Credit purchase return Account
(c) Debit Profit and Loss account, Credit purchase return Account
(d) Debit purchase return account, Credit trading Account.
Answer:
(d) Debit purchase return account, Credit trading Account.
The closing entry for transferring purchase return appearing in trial balance will be: Debit Purchase Return A/c, Credit Trading A/c
118. Ledger book is popularly known as:
(a) Secondary Book of Accounts
(b) Additional Book of Accounts
(c) Subsidiary Book of Accounts
(d) Principal Book of Accounts
Answer:
(d) Ledger book is also known as principal book.
119. A Cash Book does not record:
(a) Purchase of furniture
(b) Rent paid
(c) Salary outstanding
(d) Salary paid
Answer:
(c) Salary outstanding
Cash Book is the book in which all transaction relating to cash receipt and cash payment are recorded. Salary Outstanding will be recorded in Journal Proper, not in Cash Book because it does not include cash payment.
120. A suspense account facilitates the preparation of when the has not been tallied _______.
(a) Trial Balance, Financial Statement
(b) Financial Statement, Trial Balance
(c) Ledger, Trial Balance
(d) Journal, Trial Balance
Answer:
(b) Financial Statement, Trial Balance
A suspense account is opened when total of debit of Trial Balance does not match with the total of credit of Trial Balance and it facilitates the preparation of financial statement when the Trial Balance has not been tallied
121. What will be debited and credited if Mr. A started business with cash ₹ 2,00,000?
(a) Mr. A’s account and capital account respectively
(b) Business A/c and Cash A/c respectively
(c) Capital A/c and Cash A/c respectively
(d) Cash A/c and Capital A/c respectively.
Answer:
(d) Cash A/c and Capital A/c respectively.
Journal Entry for the transaction Cash A/c Dr. 2,00,000
To Capital A/c
122. Goods returned by business organization to suppliers noted in which books of the organization?
(a) Credit note
(b) Sales return book
(c) Debit note
(d) Purchase return book
Answer:
(d) Purchase return book
The purchase returns books records the details of goods returned by the business organization to the supplier(s). The goods purchased for cash and returned are not recorded in this book. When the goods are returned to the supplier, a debit note is sent to him indicating that his account has been debited with the amount mentioned in the debit note.
123. The balance of petty cash is _______.
(a) Expense
(b) Income
(c) Asset
(d) Liability
Answer:
(c) Asset
The general ledger account Petty Cash is reported on the balance sheet as a current asset. Often the balance in the Petty Cash account is combined with the balances in other cash accounts (such as checking accounts) and the total will be reported on the balance sheet as cash.
The Petty Cash account should be replenished just prior to issuing the financial statements so that the amount of currency and coins on hand is equal to the balance in the Petty Cash account. This also ensures that the recent petty cash disbursements are recorded in their appropriate accounts often expense accounts.
124. A firm has to take decision about the nature and extent of product differentiation and’ hence the level of selling expense in _______ market structure.
(a) Monopoly
(b) Monopolistic competitive
(c) Perfectly competitive
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(c) Perfectly competitive
Perfect competition is a market structure in which the following five criteria are met:
- All firms sell an identical product;
- All firms are price takers – they cannot control the market price of their product;
- All firms have a relatively small market share;
- Buyers have complete information about the product being sold and the prices charged by each firm;
- The industry is characterized by freedom of entry and exit.
Perfect competition is sometimes referred to as “pure competition. Thus option b is correct.
125. The trade discount received is:
(a) Real account
(b) Liability account
(c) Revenue account
(d) Not recorded in books of account
Answer:
(d) Not recorded in books of account
The Trade Discount is not recorded in the Books of A/c.
126. After preparing the trial balance the accountant finds that the total of the debit side is short by ₹ 1,000. This difference will be :
(a) Debited to suspense account
(b) Adjusted to any of the debit balance account
(c) Credited to suspense account
(d) Adjusted to any of the credit balance account
Answer:
(a) Debited to suspense account
The difference between the Debit and Credit side is transferred to the Suspense A/c.
If Debit side is short, A/c is debited
If Credit side is short, A/c is credited
127. Which of the following is not a column in a three column cash book?
(a) Petty cash column
(b) Cash column
(c) Discount column
(d) Bank column
Answer:
(a) Petty cash column
The three columns of a Three Column Cash Book are:
- Cash Column
- Discount Column
- Bank Column
128. Journal entry for goods ₹ 50 withdrawn by proprietor for personal use will be:
(a) Debit purchases A/c credit advertisement A/c ₹ 50
(b) Debit sales A/c credit drawings A/c ₹ 50
(c) Debit drawings A/c credit purchases A/c ₹ 50
(d) Debit purchases A/c credit expenses A/c ₹ 50
Answer:
(c) Debit drawings A/c credit purchases A/c ₹ 50
Journal Entry would be
Drawings A/c Dr. 50
To Purchase A/c 50
129. Credit purchase of cotton by cotton dealer worth ₹ 10,000 will be entered in:
(a) Bill Receivable Book
(b) Sales Book
(c) Purchases Book
(d) Journal Proper
Answer:
(c) Purchases Book
Credit Purchase of cotton by cotton dealer will be treated as purchase of good and hence entered in the Purchase Book.
130. The correct sequence of the following in the preparation of periodical final statements would be:
1. Preparation of Balance Sheet
2. Preparation of cash flow statement
3. Preparation of Trial Balance
4. Preparation of Profit/Loss statement The correct option is:
(a) 4, 2,1, 3
(b) 3, 4, 1, 2
(c) 2, 4, 3, 1
(d) 1, 3, 2, 4
(c) Firstly prepare trial balance then with the help of trial balance Trading and Profit and Loss A/c is prepared and then cash flow statement after that at the end Balance Sheet will be prepared.
131. The total cost of goods available for sale with a company during the current year is ₹ 12,00,000 and the total sales’during the period are ₹ 13,00,000. Gross profit margin of the company is 33.33% on cost. The closing inventory for the current year would be:
(a) ₹ 4,00,000
(b) ₹ 3,00,000
(c) ₹ 2,25,000
(d) ₹ 2,60,000
Answer:
(a) ₹ 4,00,000
Cost of goods available for sale is ₹ 12,00,000
Total Sales – 13,00,000
Gross Profit is 33.33% or \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) on cost. (Given)
Closing Inventory for current year = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) x 12,00,000
= ₹ 4,00,000
132. On 1st April, 2012 in Sethi’s ledger furniture account showed a balance of ₹ 2,00,000. On 1st October, 2012 Sethi purchased new furniture by paying ₹ 5,000 and giving old furniture where book value on 1st April, 2012 was ₹ 12,000 to the seller. Sethi provides depreciation on furniture @10% per annum on diminishing balance method. The Net Value of Furniture in Sethi’s books as on 31st March, 2013 would be:
(a) ₹ 1,85,000
(b) ₹ 1,83,960
(c) ₹ 1,84,780
(d) ₹ 2,04,400
Answer:
(c) ₹ 1,84,780
133. A chronological record of transaction may be found in:
(a) Balance sheet
(b) Trial balance
(c) Ledger
(d) Journal
Answer:
(d) Journal
Journal is primary book in which transactions are record chronologically while transactions are analytically recorder in ledger.
134. How does an overcasting of purchase day book affect the cost of sale and profit?
(a) Cost of sales is decreased while profit is increased
(b) Cost of sales is increased while profit is decreased
(c) Both cost of sales and profit are increased
(d) Cost of sales is increased, gross profit is decreased but net profit remains unaffected
Answer:
(b) Cost of sales is increased while profit is decreased
Cost of sale and profit are directly proportion when sale is increased, profit is increased and when sale is decreased, profit is decreased. So, purchase day book affect the Cost of sale and profit at decreasing point.
135. Which one of the following statement is correct?
(a) Capital of the firm is reduced by borrowing
(b) When there is no change in proprietor’s capital it is an indication of loss in business
(c) Nominal Account refer to false transactions
(d) Real accounts relate to the assets of business.
Answer:
(d) Real accounts relate to the assets of business.
‘Real Accounts refer to asset of business’. This statement is correct. Balance Sheet consist of Real and Personal A/c only not Nominal A/c
136. Which one appear in the trial balance on Debit side.
(a) Cash
(b) Sales
(c) Capital
(d) Sales returns
(i) a, b, c
(ii) b, c
(iii) a, d
(iv) None of these
Answer:
(iii) a, d
Item which are recorded on debit side of a trial balance;
- Assets
- Expenses and losses though cash is an asset having debit nature and sales return is a kind of loss having debit nature.
Hence, option (iii) a, d is correct.
137. Inventory book is used to view:
(a) Group Inventory
(b) Stock Items
(c) All of these
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) All of these
Inventory book is used to see group inventory as well as to stock items. Thus, option (c) is correct.
138. The imprest system pertain to:
(a) Purchase book
(b) Sales book
(c) Cash book
(d) Petty cash book
Answer:
(d) Petty cash book
Petty cash book is maintained on Imprest System.
139. The statement showing balance of all the ledger accounts is known as:
(a) Trial balance
(b) Balance Sheet
(c) Bank reconciliation statement
(d) Profit and loss account
Answer:
(a) Trial balance
Trial Balance is the statement that shows the balances of all ledger accounts at one place.
140. Balance of Petty Cash Book is transferred to _______.
(a) Balance Sheet
(b) P/LA/c
(c) Cash Book
(d) Trading A/c
Answer:
(a) Balance Sheet
Balance of Petty Cash Book is transferred to balance sheet. Petty cash appears within the current assets section of the balance sheet.
141. What comes in same side of Trial Balance?
(a) Capital and Drawing
(b) Furniture and Liability
(c) Asset and Expense
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Asset and Expense
Debit side of trial balance contain Assets and expenses on the others hand credit side of trial balance contains liability, capital and incomes.