Account Current – CA Foundation Accounts Study Material is designed strictly as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
Account Current – CA Foundation Accounts Study Material
Question 1.
Account Current.
Answer:
Account Current:
→ Account Current is a statement rendered by one party to other giving details of transactions with that party together with the details of interest calculation. It is prepared just like an account by providing additional columns for interest calculation on both sides i.e., debit & credit sides.
→ Account current serves the purpose that not only the other party can verify transaction but also the interest calculations. It is prepared for a particular period.
→ It can be prepared in the following 3 ways.
- Account current by products of each transaction method (it is most common).
- Account current by product of balance method. (It is followed by Banks etc.)
- Account current prepared with the help of Interest tables.
Question 2.
Red ink interest.
Answer:
Red ink interest:
→ In account current interest is calculated on every transaction from its due date to the end of that period. When the due date is not given the date of transaction itself will be taken as due date.
→ In case the due date falls beyond the end of that period, then no interest is to be given on it upto the period end.
→ But the negative interest (opposite interest) from the end of period to the due date should be calculated, & written in red ink on the side of transaction so that this Red ink products will be deducted from the other products of that side, OR alternatively to give this effect this products can be written by the same ink but on the Opposite side of that transaction.
→ Example – Account current is for the period 1.1.04 to 31.3.04. Due date of a particular transaction is say 20th April, then the red ink days (opposite days/negative days) will be 20 days.
![]()
Question 3.
Epoque or backward calculation method.
Answer:
Epoque or backward calculation method:
- In product of transaction method the days are calculated from due date to the end of period.
- Hence when due date was beyond the end of period we have taken negative days (contra product).
- In backward method the days are calculated from due date to the starting of period hence the name backward calculation.
- Ascertain closing balance before interest because product for this balance from closing date to opening date are to be calculated.
- Product on opening balance will be nil (zero) because product for this balance from opening date to opening date are to be calculated.
- The only plus point of this method is that even if due dates are beyond cut off date negative/contra days will not come.
- But while deciding whether interest is receivable or payable the interpretation will be reverse of what you have done in earlier method i.e.
- If debit products are there interest is payable and
- If credit products are there interest is recoverable.
Question 4.
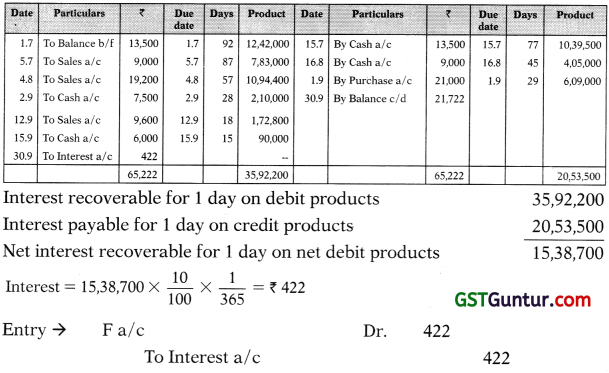
From the following information, prepare account current on 30th Sep-tember, 2011 to be submitted by M to F.
| 2011 | ||
| July 1 | Debit balance b/f | 13,500 |
| 5 | Sold goods to F | 9,000 |
| 15 | Received cash from F | 13,500 |
| August 4 | Sold goods to F | 19,200 |
| 16 | Received cash from F | 9,000 |
| September 1 | Bought goods from F | 21,000 |
| 2 | Paid cash to F | 7,500 |
| 12 | Sold goods to F | 9,600 |
| 15 | Paid cash to F | 6,000 |
Interest is to be taken into account @ 1096 per annum; it may be calculated to the nearest rupee.
Solution:
Account current rendered (sent/submitted) by ‘M’ to ‘F’ or
‘F’ in Account current with ‘M’
For the period 1.7.2011 to 30.9.2011
Question 5.
From the following particulars, calculate days for preparing an account current by product of transaction method as on 31st March, 2011
| ₹ | ||
| Jan. 1 | Opening Balance | 2,000 |
| 10 | 2 months Bill drawn | 5,000 |
| 16 | Purchased goods supplier allows 1 month credit | 3,000 |
| 29 | Sold goods on 1 month credit | 1,000 |
| Feb. 10 | Paid cash | 1,700 |
| 15 | Received cheque dated 20.2.11 | 2,500 |
| March 18 | Sold goods payment due on 25.03.11 | 6,000 |
Solution:
Calculation of Days (from the due date to the end of the period i.e. 31.3. 2011)
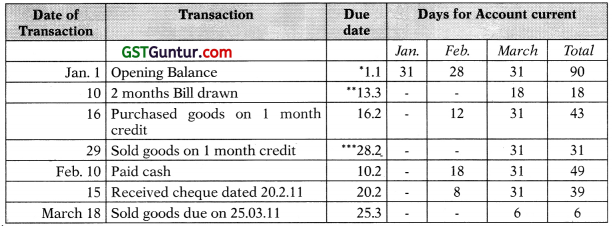
→ For opening balance 1 st Jan. will also be counted because in effect it is brought from 31st December.
→ It is bill of exchange hence 2 months + 3 days of grace are added.
→ From 29th Jan. 1 month will be completed on 29th Feb. but because Feb. 2011 do not have 29 days hence last date of the month that is 28th Feb. is taken.
![]()
Question 6.
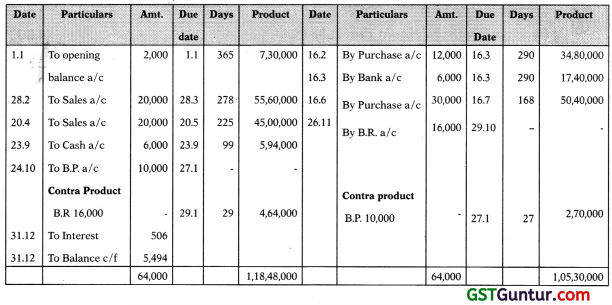
Following are the transaction between Sanjay and Ravi. Both allows one month credit to each other on sale/purchases.
| ₹ | ||
| Jan. 1 | Balance due from Sanjay | 2,000 |
| Feb. 16 | Purchased goods from him | 12,000 |
| 28 | Sold goods to him | 20,000 |
| March 16 | Received a cheque | 6,000 |
| April 20 | Sold him goods (invoiced on May 3) | 20,000 |
| June 16 | Purchased goods from him (invoiced on July 10) | 30,000 |
| Sept. 23 | Paid him cash | 6,000 |
| Oct. 24 | Accepted his bill for 3 months | 10,000 |
| Nov. 26 | Received his acceptance for 2 months | 16,000 |
Prepare an account current of Sanjay with Ravi upto 31.12.03 reckoning interest @14% p.a. on the balance due.
Solution :
Product of Transaction Method (Red Ink Interest Method)
Sanjay in Account Current with Ravi for the period 1.1.03 to 31.12.03
Working Notes:
Interest recoverable on 1,18,48,000 – 1,05,30,000 = 13,18,000
Interest = 13,18,000 x \(\frac { 14 }{ 100 }\) x \(\frac { 1 }{ 365 }\) = ₹ 506
Entry for interest due:
Sanjay a/c Dr. 506
To Interest a/c 506
Important points Regarding Due date:
1. When in case of sale, purchase, credit period is given the same will be added to date of transaction to get due date. Where invoice date is given (like in this question) the same will be taken as due date.
2. In case of bill of exchange/promissory note due date will be calculated by adding the period + 3 days of grace.
3. In case of sales/purchase return the due date of sale/purchase should be taken for return also because it is only a cancellation entry, hence interest effect should also get cancelled.
Red Interest/Contra Product: When due date of a transaction falls beyond the cut off date (i.e. 31.12.2003 in this case), there are no days from due date to cut off date rather there are reverse or opposite days from due date to cut off date. Such days are either written on same side by (-) sign or in red ink (followed by bank, hence the name red ink interest) or the same effect is created by writing the products on opposite side known as contra product.
Question 7.
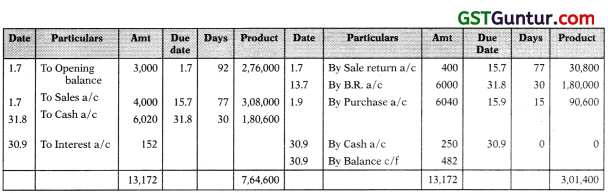
From the following Prepare account current of A in the books of B as at 30.9.2011 Interest @12% p.a.
| ₹ | ||
| July 1 | Balance due to B | 3,000 |
| 1 | A buys goods; payment due July 15 | 4,000 |
| 8 | Return of goods bought on July 1 | 400 |
| 13 | B/R from A, due August 31, discounted with banker @15% p.a. on 15th July | 6,000 |
| August 31 | B/R returned dishonoured, noting charged ₹ 20 | 20 |
| Sept. 1 | Purchases by B, payment due 15th September | 6,040 |
| 30 | A remits cash | 250 |
Solution:
Product of Balance Method not applicable in this question:
You can observe that there are transaction whose due date are different than the date of transaction, hence product of balance method cannot be applied. Because effect of a transaction on the balance will come on the date of transaction itself when we record it, whereas for interest it should be considered from the due date only ‘A’ in Account Current with ‘B’ (Product of Transaction Method) for the period 1.7.03 to 30.9.03
Calculation of Interest
Net product on which interest is recoverable = 7,64,600 – 3,01,400 = 4,63,200
Interest = 4,63,200 x \(\frac { 12 }{ 100 }\) x \(\frac { 1 }{ 365 }\) = 152
Entry for interest due:
A’s a/c Dr. 152
To Interest a/c 152
Question 8.
The following are the transactions that took place between X and Y during the period from 1st January to 30th June, 2011:
| ₹ | |
| (i) Balance due to X by Y as at 1st January | 602 |
| (ii) Sold by X to Y on 17th January | 884 |
| (iii) Goods sold by Y to X on 16th February (invoice dated 1st April) | 1,296 |
| (iv) Goods returned by X to Y on 18th February (out of goods purchased on 16th February) | 112 |
| (v) Goods sold by Y to X on 24th March (invoice dated 1st May) | 712 |
| (vi) Bill drawn by Y on X at 3 months accepted by the latter on 22nd April | 300 |
| (vii) Cash paid by X to Y on 29th April | 500 |
| (viii) Goods sold by X to Y on 17th May (invoice dated 1st June) | 542 |
| (ix) Goods sold by Y to X on 22nd June (invoice dated 1st August) | 456 |
Draw up an account current upto 30th June, 2011 to be rendered by X to Y charging interest at 15% per annum.
Solution :
Account Current by Product of Transaction Method (Epoque/Backward Calculation Method)
Y’s in Account current with X
For the period 1.1.2011 to 30.6.2011
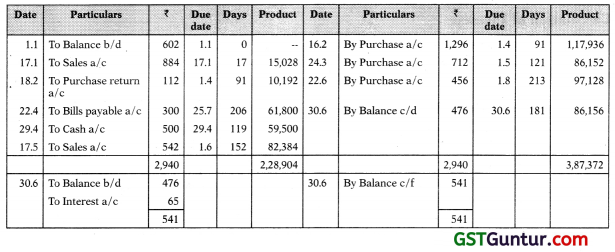
Interest recoverable on 3,87,372 – 2,28,904 = 1,58,468
Interest = 1,58,468 x \(\frac { 1 }{ 365 }\) = ₹ 65
Note:
You must have noted that in this case balance before interest is also required to be worked out at the end of the period, product on same is also calculated for 181 days i.e. 1.1.2011 to 30.6.2011. If you wish to practice, apply it on other questions and compare the result which must be same.
![]()
Question 9.
Ram had a bank balance of ₹ 20,700 in his account with SBI on 1.9.2003. His other transactions during the month of September are as follows:
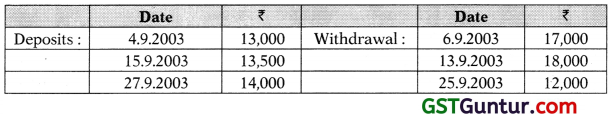
Prepare account current of Ram with SBI on 30.9.03 as per Product of Balance Method assuming interest @15% p.a.
Solution:
Account Current by Product of Balances Method
‘Ram’ in Account Current with ‘SBI’ (Ram’s a/c in the books of ‘SBI’)
for the period 1.9.03 to 30.9.03
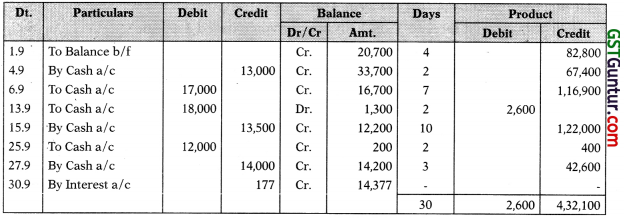
Working Notes:
Calculation of Interest
Net Interest payable on 4,32,100 – 2,600 = 4,29,500
Interest = 4,29,500 x \(\frac { 15 }{ 100 }\) x \(\frac { 1 }{ 365 }\) = ₹ 177
Entry for interest due:
Interest a/c Dr. 177
To Ram a/c 177
Explanation:
- This is passbook i.e. customers a/c in the books of bank exact opposite of bank a/c in customers book.
- Here days are the days for which that balance exist. For any transaction day is completed on next date like for transaction of 4.9, 1 day is completed on 5.9.
- Hence upto 4.9 previous balance is considered and 1 day of new balance ₹ 33,700 is counted from 5.9, so on and so forth.
Question 10.
Following transactions took place between X & Y during the months of April, 1999.
| Date | Details | Amount (₹) |
| 01/04/99 | Amount payable by X to Y | 10,000 |
| 07/04/99 | Received acceptance of X to Y for 2 months | 5,000 |
| 10/04/99 | Bill Receivable (Accepted by Y on 7/2/99) is honoured on this due date | 10,000 |
| 10/04/99 | X sold goods to Y (invoice dt. 10/5/99) | 5,000 |
| 12/04/99 | X received cheque from Y (dated 15/5/99) | 7,500 |
| 15/04/99 | Y sold goods to X (invoice dt. 15/5/99) | 6,000 |
| 20/04/99 | X returned goods sold by Y on 15/4/99 | 1,000 |
You are required to make an account current by products method to be ren-dered by X to Y as on 30/04/99 taking interest into a/c @ 1096 p.a.
Solution:
Product of Transaction Method
Y’s in Account current with X’s
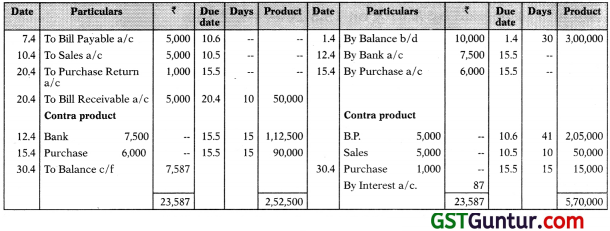
Interest payable on 5,70,000 – 2,52,500 = 3,17,500
Interest = 3,17,500 x \(\frac { 10 }{ 100 }\) x \(\frac { 1 }{ 365 }\) = ₹ 87
Special Note: In case of transactions where invoice date is given, but no credit period specified, take date of invoice as the due date.
![]()
Question 11.
Mr. A owed ₹ 4,000 on 1st January, 2004 to Mr. X. The following transactions took place between them. It is agreed between the parties that interest @10% p.a. is to be calculated on all transactions.
| ₹ | |
| 15 January, 2004 Mr. X sold goods to Mr. A | 2,230 |
| 29 January, 2004 Mr. X bought goods from Mr. A | 1,200 |
| 10 February, 2004 Mr. A paid cash to Mr. X | 1,000 |
| 13 March, 2004 Mr. A accepted a bill drawn by Mr. X for one month | 2,000 |
They agree to settle their complete accounts by one single payment on 15th March, 2004. Prepare Mr. A in Account Current with Mr. X and ascertain the amount to be paid.
Ignore days of grace.
Solution:
Mr. A in Account Current with Mr. X from 1.1.2004 to 15.3.2004
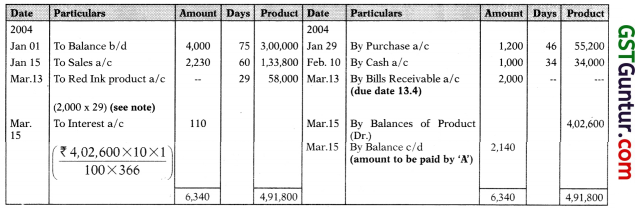
Amount to be paid by A to X on 15.3.2004 = ₹ 2,140
Note:
Red ink interest product (contra product) are from 16.3.2004 to 13.4.2004.
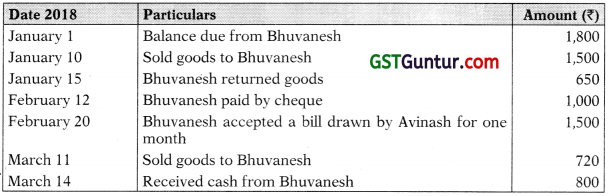
Question 12.
From the following prepare an account current, as sent by Avinash to Bhuvanesh on 31st March, 2018 by means of products method charging in-terest @5% per annum:
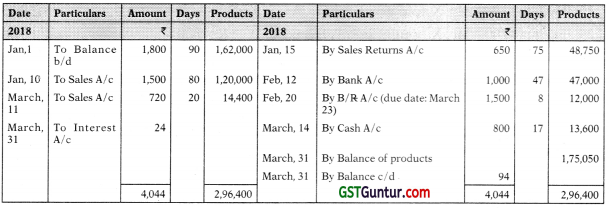
Solution:
Mr. XY in Account Current with Mr. AB
(Interest upto 31st October at 5% p.a.)
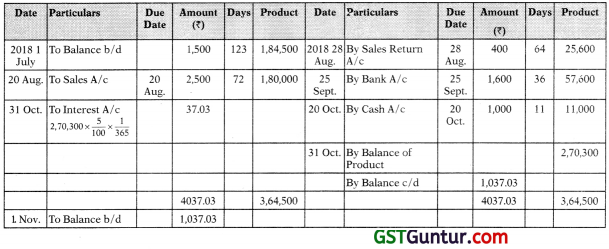
Question 13.
From the following particulars prepare an account current, as sent by Mr. AB to Mr. XY as on 31st October, 2018 by means of product method charging interest @5% p.a.
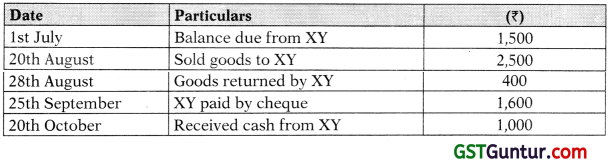
Solution:
Mr. XY in Account Current with Mr. AB
(Interest upto 31st October at 5% p.a.)
True or False
Question 1.
In Account Current, red-ink interest is treated as negative interest.
Answer:
True: Red-ink interest is treated as negative interest.
Question 2.
There are two ways of preparing an account current.
Answer:
False: There are three ways of preparing an Account Current:
- With help of interest table
- By means of products and
- By means of products of balances.
![]()
Question 3.
In case the due date of a bill falls after the date of closing the account, the interest from the date of closing to such due date is known as Red-Ink interest.
Answer:
True: In case the due date of a bill falls after the date of closing the account, the interest from the date of closing to such due date is known as Red-Ink interest.
